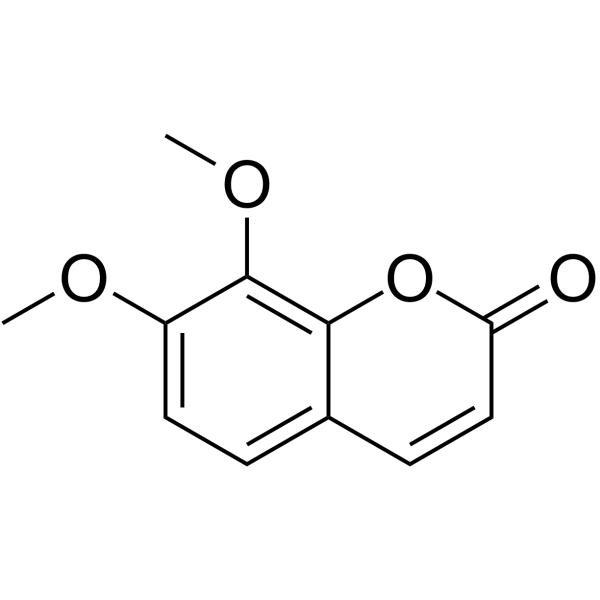
7,8-Dimethoxycoumarin
CAS No. 2445-80-9
7,8-Dimethoxycoumarin( Daphnetin dimethyl ether | 7,8-dimethoxychromen-2-one )
Catalog No. M29126 CAS No. 2445-80-9
7,8-Dimethoxycoumarin is a natural product isolated from Artemisia caruifolia and Wikstroemia indica.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 43 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 55 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name7,8-Dimethoxycoumarin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description7,8-Dimethoxycoumarin is a natural product isolated from Artemisia caruifolia and Wikstroemia indica.
-
Description7,8-Dimethoxycoumarin is a natural product isolated from Artemisia caruifolia and Wikstroemia indica.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsDaphnetin dimethyl ether | 7,8-dimethoxychromen-2-one
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2445-80-9
-
Formula Weight206.197
-
Molecular FormulaC11H10O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESCOc1ccc2ccc(=O)oc2c1OC
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Pipoxizine
Pipoxizine has an antagonistic effect on histamine-induced bronchoconstriction and may be used in the study of asthma disease.
-
Type A Allatostatin ...
Type A Allatostatin II
-
[Lys0] g-1-MSH, amid...
[Lys0] g-1-MSH, amide



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


