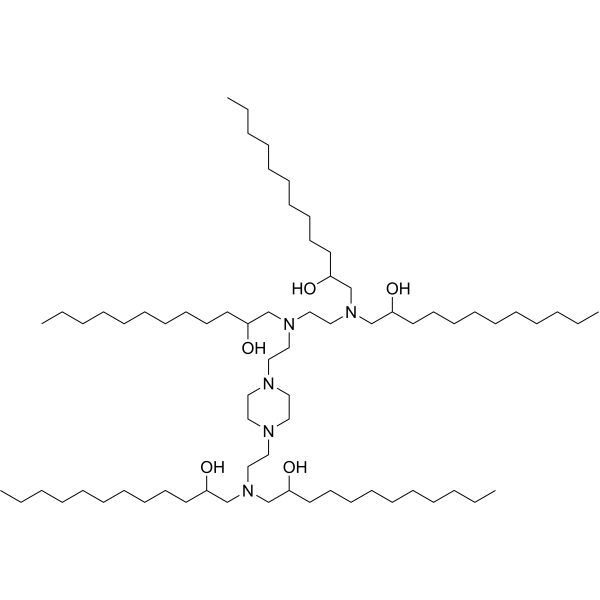
C12-200
CAS No. 1220890-25-4
C12-200( —— )
Catalog No. M28191 CAS No. 1220890-25-4
C12-200 is a benchmark ionizable cationic lipidoid along with helper lipids. C12-200 is commonly used for mRNA delivery.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 145 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 69 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 117 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 188 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 346 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 576 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 816 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameC12-200
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionC12-200 is a benchmark ionizable cationic lipidoid along with helper lipids. C12-200 is commonly used for mRNA delivery.
-
DescriptionC12-200 is a benchmark ionizable cationic lipidoid along with helper lipids. C12-200 is commonly used for mRNA delivery.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorCB2
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1220890-25-4
-
Formula Weight1136.93
-
Molecular FormulaC70H145N5O5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (87.96 mM)
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Andrew John Eatherton, et al. Pyrimidine derivatives and their use as cb2 modulators. WO2004018433.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Prosaptide, wild typ...
Prosaptide, wild type
-
Pentyl dodecanoate
Pentyl dodecanoate (Pentyl laurate) is an active substance isolated from wine yeast oil that can be used to reduce hair loss and improve hair growth.
-
6-Methoxykaempferol ...
6-Methoxykaempferol 3-O-rutinoside is a natural product.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


