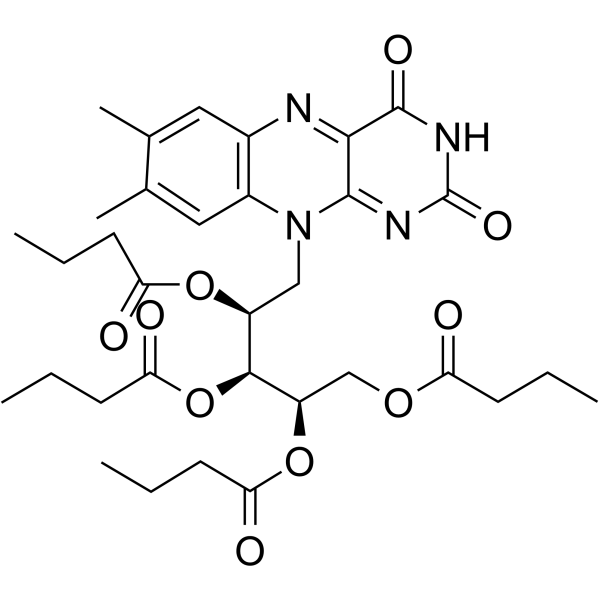
Riboflavin Tetrabutyrate
CAS No. 752-56-7
Riboflavin Tetrabutyrate( —— )
Catalog No. M26805 CAS No. 752-56-7
Riboflavin Tetrabutyrate is a lipophilic flavin derivative. Riboflavin Tetrabutyrate has antioxidative and lipid peroxide-removing activity.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 48 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 31 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameRiboflavin Tetrabutyrate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionRiboflavin Tetrabutyrate is a lipophilic flavin derivative. Riboflavin Tetrabutyrate has antioxidative and lipid peroxide-removing activity.
-
DescriptionRiboflavin Tetrabutyrate is a lipophilic flavin derivative. Riboflavin Tetrabutyrate has antioxidative and lipid peroxide-removing activity.(In Vitro):Riboflavin Tetrabutyrate is suppressive against both NADPH-coupled and ascorbate-induced microsomal lipid peroxidation. Riboflavin Tetrabutyrate inhibits oxygen uptake by lipid peroxidation. Riboflavin Tetrabutyrate seems to exhibit its antioxidative action at or after the hydrogen atom is abstracted as a free radical from an active methylene group of polyunsaturated fatty acids during the process of enzymic oxidation-reduction reaction .(In Vivo):Riboflavin Tetrabutyrate might improve the metabolism of lipids in patients suffering from atherosclerosis, diabetes, fatty liver, and so on through the inhibition of lipid peroxide, resulting in a decrease of the elevated serum lipid. The increase in hepatic 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase activity suggests that prolonged Riboflavin Tetrabutyrate administration induces an increased beta-oxidation of fatty acid in the liver. Feeding of Riboflavin Tetrabutyrate causes an increase in the hepatic activity of 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase by 50% of the control level, while the activities of renal 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase and of hepatic and renal acyl-CoA synthetase and acyl-CoA dehydrogenase remain unaffected .
-
In VitroRiboflavin Tetrabutyrate inhibits oxygen uptake by lipid peroxidation. Riboflavin Tetrabutyrate is suppressive against both NADPH-coupled and ascorbate-induced microsomal lipid peroxidation. Riboflavin Tetrabutyrate seems to exhibit its antioxidative action at or after the hydrogen atom is abstracted as a free radical from an active methylene group of polyunsaturated fatty acids during the process of enzymic oxidation-reduction reaction.
-
In VivoRiboflavin Tetrabutyrate might improve the metabolism of lipids in patients suffering from atherosclerosis, diabetes, fatty liver and so on through the inhibition of lipid peroxide, resulting in the decrease of the elevated serum lipid. Feeding of Riboflavin Tetrabutyrate results in an increase in the hepatic activity of 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase by 50% of the control level, while the activities of renal 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase and of hepatic and renal acyl-CoA synthetase and acyl-CoA dehydrogenase remain unaffected. The increase in hepatic 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase activity suggests that prolonged Riboflavin Tetrabutyrate administration results in an increased beta-oxidation of fatty acid in the liver .
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayImmunology/Inflammation
-
TargetROS
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number752-56-7
-
Formula Weight656.733
-
Molecular FormulaC33H44N4O10
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (152.27 mM)
-
SMILESCCCC(=O)OC[C@@H](OC(=O)CCC)[C@@H](OC(=O)CCC)[C@H](Cn1c2cc(C)c(C)cc2nc2c(O)nc(=O)nc12)OC(=O)CCC
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Itkin M, et al. The biosynthetic pathway of the nonsugar, high-intensity sweetener mogroside V from Siraitia grosvenorii.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Nov 22;113(47):E7619-E7628.
molnova catalog



related products
-
4-Aminophenol
4-Aminophenol (or para-aminophenol or p-aminophenol) is the organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4OH. Typically available as a white powder it is commonly used as a developer in black-and-white film marketed under the name Rodinal.
-
ROS kinases-IN-1
ROS kinases-IN-1 is a ROS tyrosine kinase inhibitor with IC50 value of 1.22 μM. ROS kinases-IN-1 shows anti-tumor activity.
-
SFI003
SFI003 is a novel SRSF3 inhibitor that exerts anticancer activity against colorectal cancer by modulating the SRSF3 / DHCR24 / ROS axis and driving apoptosis in CRC cells through the SRSF3 / DHCR24 / reactive oxygen species (ROS) axis.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


