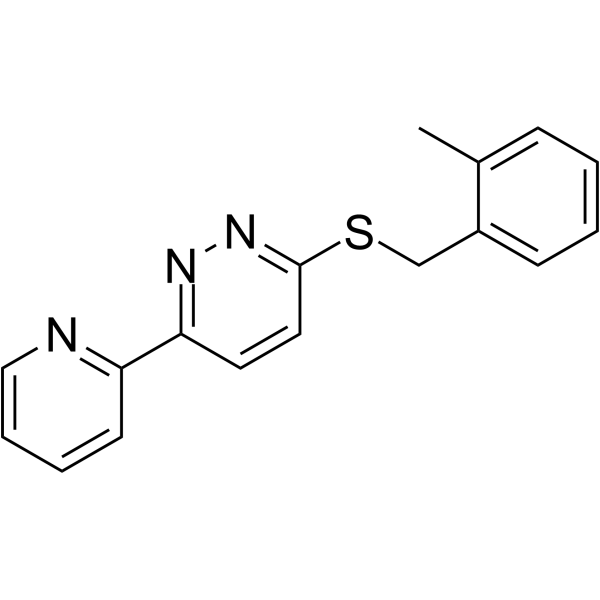
LDN-212320
CAS No. 894002-50-7
LDN-212320( LDN/OSU-0212320 | LDN-0212320 | OSU-0212320 )
Catalog No. M26737 CAS No. 894002-50-7
LDN-212320 is a glutamate transporter EAAT2 activator. It also enhances EAAT2 levels by > 6 fold at concentrations < 5 μM after 24 h.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 54 | In Stock |


|
| 2MG | 31 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 49 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 85 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 179 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 291 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 454 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 649 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameLDN-212320
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionLDN-212320 is a glutamate transporter EAAT2 activator. It also enhances EAAT2 levels by > 6 fold at concentrations < 5 μM after 24 h.
-
DescriptionLDN-212320 is a glutamate transporter EAAT2 activator. It also enhances EAAT2 levels by > 6 fold at concentrations < 5 μM after 24 h.(In Vitro):LDN/OSU-0212320 enhanced EAAT2 protein levels and glutamate uptake function but did not affect EAAT1 or EAAT3 protein levels and it also increased EAAT2 protein levels in a dose-dependent (EC50: 1.83 ± 0.27 μM) and time-dependent manner. LDN/OSU-0212320 treatment markedly prevented neuronal loss and degeneration, as assessed by MAP2 immunostaining .(In Vivo):After LDN/OSU-0212320(a single i.p.; 40-mg/kg) treatment, EAAT2 protein levels and associated glutamate uptake increased by approximately 1.5- to 2-fold at 2 hours and by approximately 2- to 3-fold between 8 and 24 hours after injection. Even 72 hours after injection, an approximately 1.5-fold increase in EAAT2 protein levels could still be detected (data not shown). LDN/OSU-0212320–induced EAAT2 protein levels and glutamate uptake was dose-dependent .
-
In Vitro——
-
In VivoLDN-212320 (10 or 20 mg/kg, i.p) significantly attenuates formalin-evoked nociceptive behavior. LDN-212320 (10 or 20 mg/kg, i.p) significantly reverses formalin-induced impaired hippocampal-dependent behavior. In addition, LDN-212320 (10 or 20 mg/kg, i.p) increases GLT-1 expressions in the hippocampus and ACC.LDN-212320 (20 mg/kg, i.p) significantly reduced formalin induced-ERK phosphorylation, a marker of nociception, in the hippocampus and ACC. Animal Model:Mice.Dosage:10 or 20 mg/kg.Administration:IP 24 h before the injection of formalin.Result:Significantly attenuated licking and biting behavior during both phases 1 and 2 in a dose-dependent manner compared to formalin-injected mice.Significantly (P < 0.01 or P < 0.001) reduced the licking and biting behavior.Significantly increased preference for the displaced object (F3, 13 = 28.03, P < 0.01) compared to formalin-injected mice.Significantly (P < 0.001) increased interaction time with the displaced object compared to formalin-injected mice.
-
SynonymsLDN/OSU-0212320 | LDN-0212320 | OSU-0212320
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorNK2
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number894002-50-7
-
Formula Weight293.39
-
Molecular FormulaC17H15N3S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (170.42 mM)
-
SMILESCc1ccccc1CSc1ccc(nn1)-c1ccccn1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Pluck G. Preliminary Validation of a Free-to-Use, Brief Assessment of Adult Intelligence for Research Purposes: The Matrix Matching Test. Psychol Rep. 2018 Jan 1:33294118762589.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Furnidipine
Furnidipine significantly reduced AoD and AF and had antiarrhythmic and cardioprotective effects at low doses in a rat model.
-
(1R,2R)-ML-SI3
(1R,2R)-ML-SI3 ((-)-trans-ML-SI3) is a selective TRPML1, TRPML2, and TRPML3 inhibitor for the study of neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases.
-
Zederone
Zederone has anti-bacterial activity,it inhibits gram-positive bacteria activity. Zederone induces hepatotoxicity implicated the induction of Cyps, which leads to the formation of biological reactive metabolites and that cause the oxidative stress and liver cell injuries.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


