Coelenterazine h
CAS No. 50909-86-9
Coelenterazine h( 2-Deoxycoelenterazine | CLZN-h )
Catalog No. M24471 CAS No. 50909-86-9
Coelenterazine H is a synthetic derivative of coelenterazine (a light-emitting biomolecule).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 217 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 353 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 582 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 808 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 1088 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 1460 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCoelenterazine h
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCoelenterazine H is a synthetic derivative of coelenterazine (a light-emitting biomolecule).
-
DescriptionCoelenterazine H is a synthetic derivative of coelenterazine (a light-emitting biomolecule).Coelenterazine h is more sensitive to Ca 2+ than is the native complex, thus providing a valuable tool for measuring small changes in Ca 2+ concentrations.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms2-Deoxycoelenterazine | CLZN-h
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number50909-86-9
-
Formula Weight407.46
-
Molecular FormulaC26H21N3O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
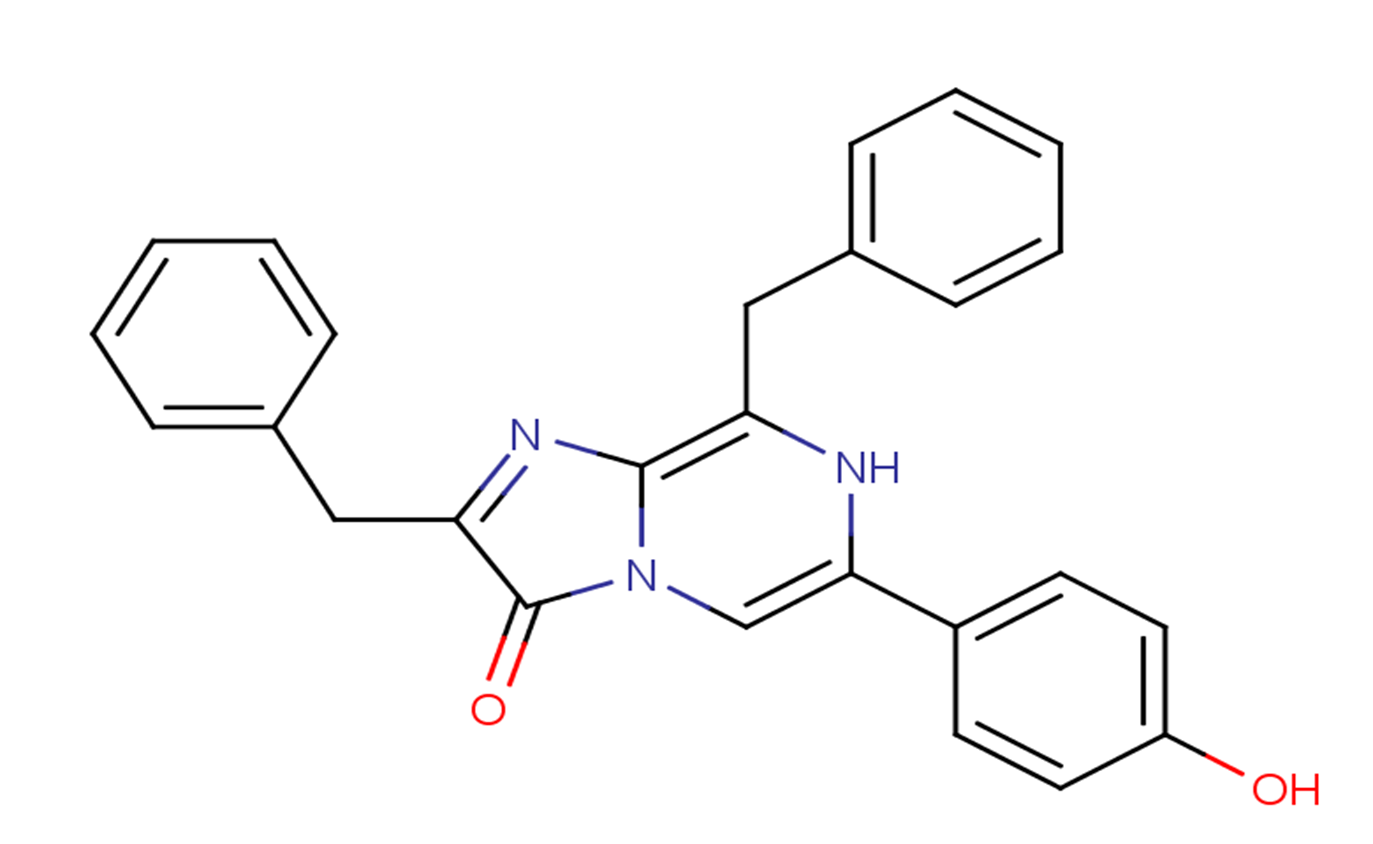
SMILESOC(C=C1)=CC=C1C2=CN(C(C(CC3=CC=CC=C3)=N4)=O)C4=C(N2)CC5=CC=CC=C5
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
4-Hydroxy-3-Nitroben...
4-Hydroxy-3-Nitrobenzyl Alcohol is a marine derived natural products found in Phidolopora pacifica.
-
TH5487
TH5487 is an potent inhibitor of 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 (OGG1)( IC50 of 342 nM).
-
AC-PHE-OME
AC-PHE-OME (Methyl N-acetyl-L-phenylalaninate) is a marine derived natural products found in Family Jaspidae.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


