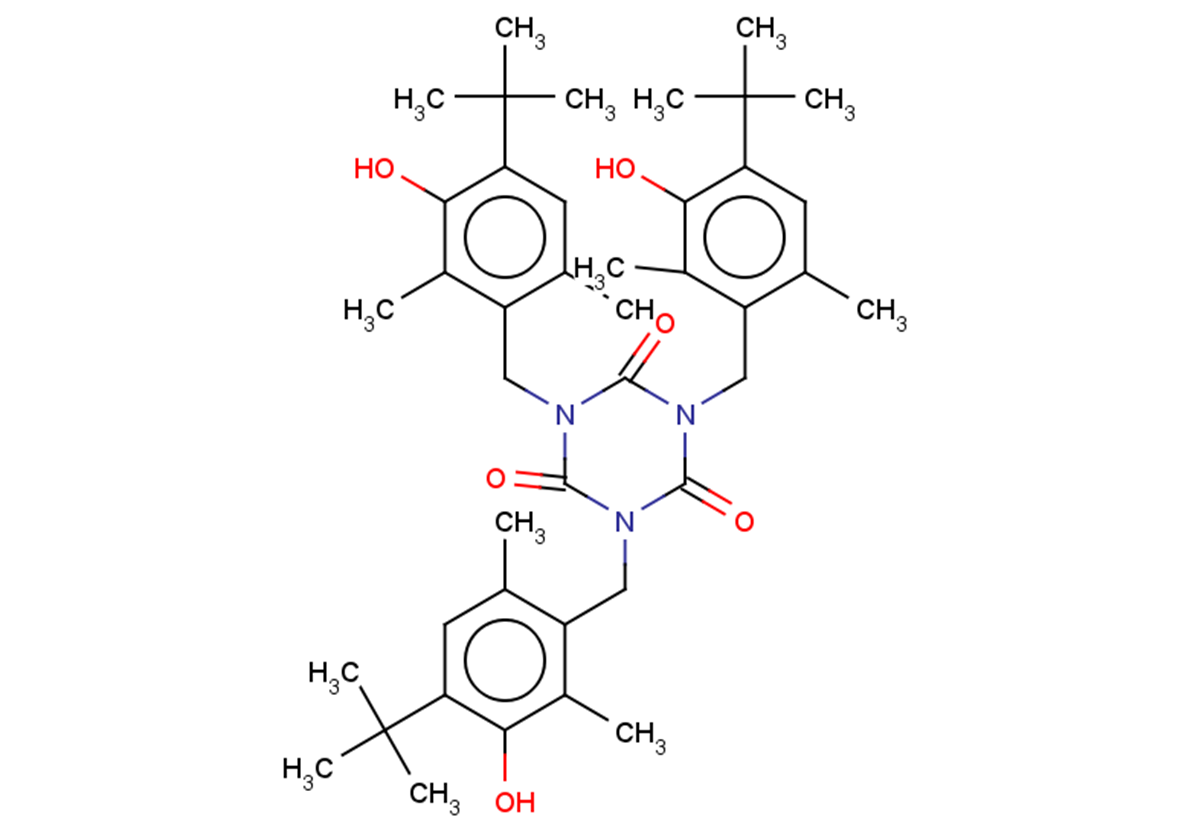
Cyanox CY 1790
CAS No. 40601-76-1
Cyanox CY 1790( Irganox 3790 | Irganox-3790 )
Catalog No. M24366 CAS No. 40601-76-1
Cyanox CY 1790 is an agent with antioxidant activity.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 27 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCyanox CY 1790
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCyanox CY 1790 is an agent with antioxidant activity.
-
DescriptionCyanox CY 1790 is an agent with antioxidant activity.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsIrganox 3790 | Irganox-3790
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number40601-76-1
-
Formula Weight699.92
-
Molecular FormulaC42H57N3O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:Soluble
-
SMILESCC(C)(C)c(cc(C)c(CN(C(N(Cc1c(C)c(O)c(C(C)(C)C)cc1C)C(N1Cc2c(C)c(O)c(C(C)(C)C)cc2C)=O)=O)C1=O)c1C)c1O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Arroyo DA, Kirkby LA, Feller MB. Retinal Waves Modulate an Intraretinal Circuit of Intrinsically Photosensitive Retinal Ganglion Cells. J Neurosci. 2016 Jun 29;36(26):6892-905. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0572-16.2016.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Naptalam
Naptalam is an herbicide.Naptalam is a dicarboxylic acid monoamide which results from addition of one equivalent of 1-naphthylamine to phthalic anhydride. It is a dicarboxylic acid monoamide, a carboxylic acid and a N-(1-naphthyl)carboxamide.
-
Angelicain
Angelicain is a constituent of Cimicifuga foetida with anti-inflammatory activity.
-
Chikusetsusaponin IV
Chikusetsusaponin IV might relieve cutaneous symptoms caused by excessive apoptotic cell death in the skin through the Fas/FasL pathway.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


