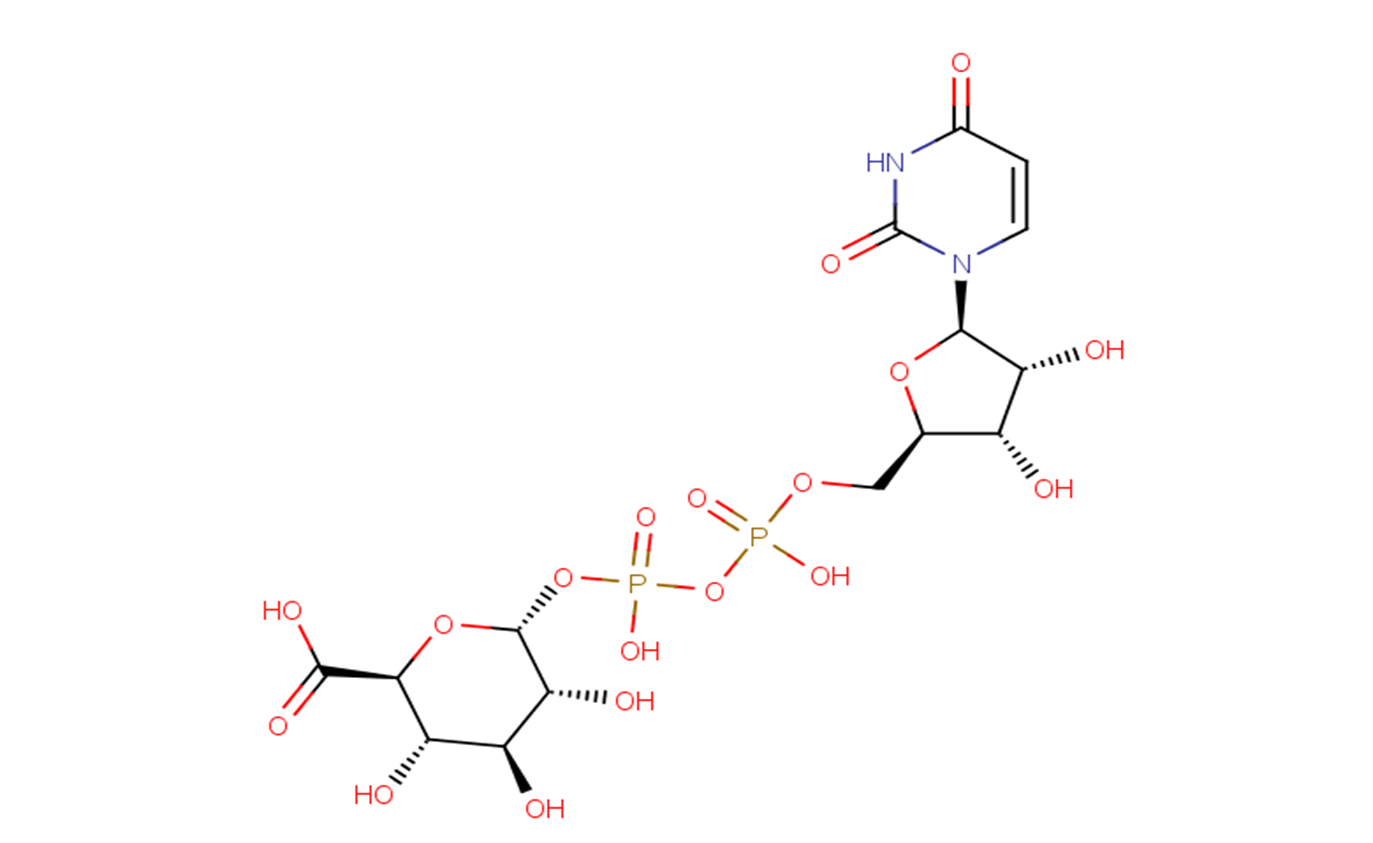
UDP-g acid
CAS No. 2616-64-0
UDP-g acid( —— )
Catalog No. M24169 CAS No. 2616-64-0
UDP-g acid is a sugar used in the production of polysaccharides and is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of ascorbic acid.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 121 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 186 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 265 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 473 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 674 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 918 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameUDP-g acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionUDP-g acid is a sugar used in the production of polysaccharides and is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of ascorbic acid.
-
DescriptionUDP-g acid is a sugar used in the production of polysaccharides and is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of ascorbic acid.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2616-64-0
-
Formula Weight580.29
-
Molecular FormulaC15H22N2O18P2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10 mM
-
SMILESC1=CN(C(=O)NC1=O)[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)COP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)O[C@@H]3[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O3)C(=O)O)O)O)O)O)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
β-lonone
β-lonone is an end-ring analog of β-carotenoids which widely distributed in fruit and vegetableswith?anti-proliferative anti-metastatic.
-
PACAP-38 (31-38), hu...
PACAP-38 (31-38), human, mouse, rat demonstrates potent, efficacious, and sustained stimulatory effects on sympathetic neuronal NPY and catecholamine production.
-
L-JNKI-1
L-JNKI-1 is a cell-permeable peptide inhibitor specific for JNK, it has been shown to effectively inhibit JNK activity in in vivo studies.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


