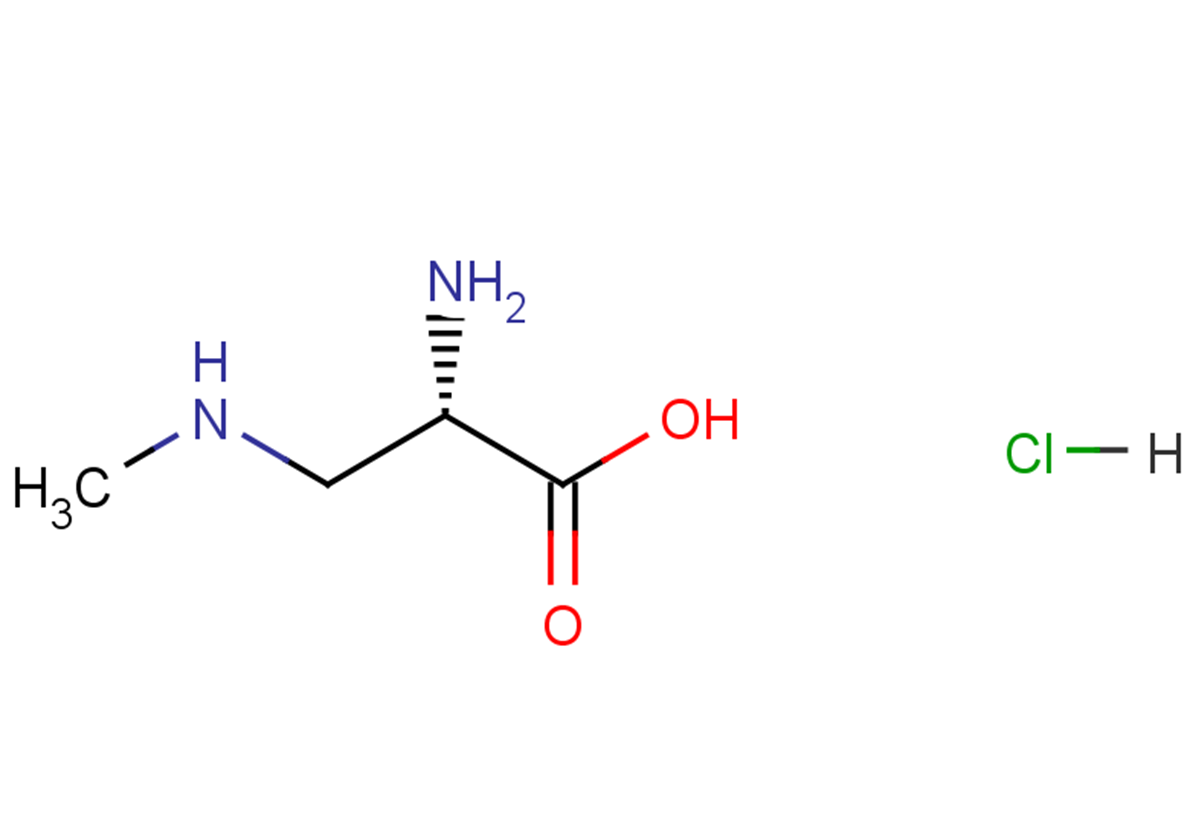
L-BMAA hydrochloride
CAS No. 16012-55-8
L-BMAA hydrochloride( β-N-methylamino-L-alanine hydrochloride )
Catalog No. M23698 CAS No. 16012-55-8
L-BMAA hydrochloride is a neurotoxin produced by cyanobacteria.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 50 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 79 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 103 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 166 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameL-BMAA hydrochloride
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionL-BMAA hydrochloride is a neurotoxin produced by cyanobacteria.
-
DescriptionL-BMAA hydrochloride is a neurotoxin produced by cyanobacteria. L-BMAA hydrochloride could cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and possibly other neurodegenerative diseases.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonymsβ-N-methylamino-L-alanine hydrochloride
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptorothers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number16012-55-8
-
Formula Weight154.6
-
Molecular FormulaC4H11ClN2O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:Soluble
-
SMILESN[C@@H](CNC)C(O)=O.[H]Cl
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Caller T, et, al. The Potential Role of BMAA in Neurodegeneration. Neurotox Res. 2018 Jan; 33(1): 222-226.
molnova catalog



related products
-
11-Oxomogroside IV
11-Oxomogroside IV is a natural product.
-
MRGPRX1 agonist 1
MRGPRX1 agonist 1 is a highly potent MRGPRX1 (Mas-related G-protein-coupled receptor X1)agonist(EC50 of 50 nM).
-
Smurf1-IN-A01
Smurf1-IN-A01 is a ubiquitin ligase Smad ubiquitination regulatory factor-1 inhibitor (kd: 3.664 nM).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


