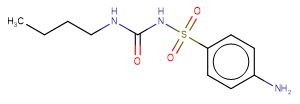
Carbutamide
CAS No. 339-43-5
Carbutamide( —— )
Catalog No. M21644 CAS No. 339-43-5
Carbutamide is a sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent with hypoglycemic activity.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 30 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 49 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 82 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCarbutamide
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCarbutamide is a sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent with hypoglycemic activity.
-
DescriptionCarbutamide is a sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent with hypoglycemic activity.
-
In Vitro——
-
In VivoCarbutamide is a sulfonylurea derivative that will cause hypoglycemia when administered by mouth to normal animals.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number339-43-5
-
Formula Weight271.34
-
Molecular FormulaC11H17N3O3S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:260 mg/mL?(958.21 mM)
-
SMILESCCCCNC(=O)NS(=O)(=O)c1ccc(N)cc1
-
Chemical NameBenzenesulfonamide 4-amino-N-((butylamino)carbonyl)-
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Ranita AimanR D KULKARNI.The Effect of Human Plasma on the Glucose Uptake of the Rat Diaphragm Before and After Administration of Carbutamide.Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Dec;12(4):475-8.
molnova catalog



related products
-
YX-2-107
YX-2-107 is a selective and potent CDK6-degrading PROTAC with an IC50 value of 4.4 nM.YX-2-107 inhibits RB phosphorylation and FOXM1 expression in vitro, and inhibits the development of Ph+ ALL in rats.
-
Mahuannin E
Mahuannin E.
-
Crenulatin
Crenulatin has dual- direction effects on apoptosis of cerebral microvascular endothelial cells, inhibitive effect in 25 mg/L and stimulative effect in 100 mg/L group, respectively; the mechanism is related to the alterations of Fas/Bcl-2 expression and caspase-3 activity.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


