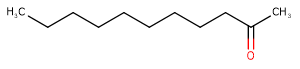
Methylnonylketone
CAS No. 112-12-9
Methylnonylketone( 2-Undecanone )
Catalog No. M21330 CAS No. 112-12-9
Methylnonylketone is a natural non-toxic insect repellant compound.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 27 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameMethylnonylketone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionMethylnonylketone is a natural non-toxic insect repellant compound.
-
DescriptionMethylnonylketone is a natural non-toxic insect repellant compound.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms2-Undecanone
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number112-12-9
-
Formula Weight170.29
-
Molecular FormulaC11H22O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (587.20 mM)
-
SMILESCCCCCCCCCC(C)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
Docosyl (2E)-3-(3,4-...
(E)-Docosyl caffeate (compound 1) can be isolated from the halophytic plant Halocnemum strobilaceum.
-
3-(Methylthio)propio...
3-methylthiopropionate is one of the metabolites of methionine (especially of D-methionine). Cultures of Streptomyces lincolnensis accumulated 3-methylthioacrylic acid in amounts directly related to the concentration of methionine in the medium. The first intermediate in the pathway may be the keto acid which is then oxidatively decarboxylated to 3-methylthiopropionic acid.
-
N-Formyl-Met-Ala-Ser
N-Formyl-Met-Ala-Ser is a peptide, binds to formyl peptide receptors on neutrophils.N-Formyl-Met-Ala-Ser Peptide (fMet-Ala-Ser) binds to formyl peptide receptors on neutrophils. N-Formylmethionine-containing peptides including the most potent and known member, N-formyl-Met-Leu-Phe (FMLP or fMet-Leu-Phe) stimulate human neutrophils by a receptor-dependent mechanism.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


