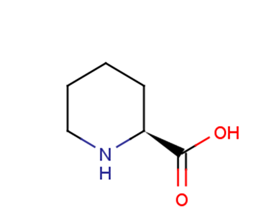
L-Pipecolic acid
CAS No. 3105-95-1
L-Pipecolic acid( H-HoPro-OH | L-Homoproline )
Catalog No. M19590 CAS No. 3105-95-1
L-Pipecolic acid is a breakdown product of lysine accumulates in body fluids of infants with generalized genetic peroxisomal disorders such as Zellweger syndrome neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 30 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameL-Pipecolic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionL-Pipecolic acid is a breakdown product of lysine accumulates in body fluids of infants with generalized genetic peroxisomal disorders such as Zellweger syndrome neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy.
-
DescriptionL-Pipecolic acid is a breakdown product of lysine accumulates in body fluids of infants with generalized genetic peroxisomal disorders such as Zellweger syndrome neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsH-HoPro-OH | L-Homoproline
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number3105-95-1
-
Formula Weight129.16
-
Molecular FormulaC6H11NO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 10 mM;Water: Soluble
-
SMILESOC(=O)[C@@H]1CCCCN1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Mihalik SJ et al. Peroxisomal L-pipecolic acid oxidation is deficient in liver from Zellweger syndrome patients. Pediatr Res. 1989 May;25(5):548-52.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Spinacine
Spinacine is a condensation product of formaldehyde and histidine and an endogenous metabolite.
-
2-Methylcyclohexanon...
2-Methylcyclohexanone is an endogenous metabolite.
-
Ternidazole hydrochl...
Ternidazole hydrochloride (Ternidazole HCl) is a 5-nitroimidazole antibiotic with antimicrobial antioxidant and antiprotozoal activity.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


