Traumatic Acid
CAS No. 6402-36-4
Traumatic Acid( —— )
Catalog No. M18942 CAS No. 6402-36-4
Traumatic Acid is a product of the hydroperoxide lyase pathway in plants. Potential as a wound healing agent that stimulates cell division near a wound site to form a protective callus.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 48 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 32 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 51 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 71 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameTraumatic Acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionTraumatic Acid is a product of the hydroperoxide lyase pathway in plants. Potential as a wound healing agent that stimulates cell division near a wound site to form a protective callus.
-
DescriptionTraumatic Acid is a product of the hydroperoxide lyase pathway in plants. Potential as a wound healing agent that stimulates cell division near a wound site to form a protective callus.
-
In VitroTraumatic Acid (0.1, 1 μM; 5 days) significantly increases cell number in fibroblasts.Traumatic Acid (0.1, 1 μM; 5 days) increases content of GPX activity and reduced glutathione, as well as decreases membrane phospholipid peroxidation in fibroblasts.Traumatic Acid (0.1, 1 μM; 5 days) enhances the production and secretion of medium collagen in medium of fibroblasts.Traumatic Acid (100, 200, 400, 600 μM; 48 h) significantly decreases live cell number, especially after 48h treatment at 100μM and 200μM in MCF-7 cells.Traumatic Acid (50-600 μM; 24, 48 h) causes dose-and time-dependent reduction in cell viability and induces apoptosis in MCF-7 cells.Traumatic Acid (50-200 μM; 24, 48 h) results in an oxidative damage of protein in MCF-7 cells.Traumatic Acid (100, 200 μM; 24, 48 h) efficiently enhances oxidative stress level in MCF-7 cells.Cell Proliferation AssayCell Line:Fibroblasts Concentration:0.1, 1 μM Incubation Time:5 days Result:Caused a significant increase in cell number, especially on day 1 at a concentration of 1 μM.Increased cell number of 133 % and 118 % compared to the untreated control cells for concentrations of 1 and 0.1 μM, respectively.Cell Viability Assay Cell Line: Fibroblasts Concentration:0.1, 1 μM Incubation Time:5 days Result:Increased total protein content of 183 % and 90% compared to the control at concentrations of 1 and 0.1 μM on day 1.Increased collagen content of 72 % at 0.1 μM (on the day 3) and of 51 % at 1 μM (on the day 1) compared to the control.Increased GPX activity by 111 % and 97 % at concentrations of 1 and 0.1 μM compared to the control.Increased content of reduced glutathione of 86 % and 80% at 0.1 and 1 μM, respectively.Decreased membrane phospholipid peroxidation.Cell Viability Assay Cell Line:MCF-7 cells Concentration:100, 200, 400, 600 μM Incubation Time:48 h Result:Decreasd live cell number of about 76% at 100 μM concentration.Cell Viability Assay Cell Line:MCF-7 cells Concentration:50-200 μMIncubation Time:24, 48 h Result: Increased thiol group content of 167% at 100μM and 24 h.Cell Viability Assay Cell Line:MCF-7 cells Concentration:100, 200 μM Incubation Time:24, 48 h Result:Increased the amount of ROS.Apoptosis Analysis Cell Line:MCF-7 cells Concentration:50-600 μM Incubation Time:24, 48 h Result:Increased level of apoptosis in a time- and dose-dependent manner.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number6402-36-4
-
Formula Weight228.28
-
Molecular FormulaC12H20O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 250 mg/mL (1095.15 mM)
-
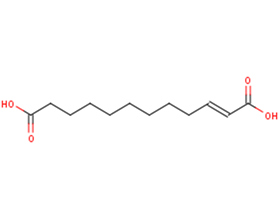
SMILESC(CCCCC(=O)O)CCC/C=C/C(=O)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Vick, B.A. Oxygenated fatty acids of the lipoxygenase pathway. Lipid Metabolism in Plants 167-191 (1993).
molnova catalog



related products
-
Kauniolide
Kauniolide(81066-45-7) is a natural compound.
-
Fmoc-N(Hmb)-Gly-OH
Fmoc-N(Hmb)-Gly-OH (Fmoc-(Hmb)Gly-OH) is a glycine derivative that can be used to synthesize peptide compounds.
-
Butanoic acid, 4-[[2...
Butanoic acid, 4-[[2-(2,6-dioxo-3-piperidinyl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3-dioxo-1H-isoindol-4-yl]amino]- is a Cereblon ligand with alkyl linker and terminal acid for onward chemistry.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


