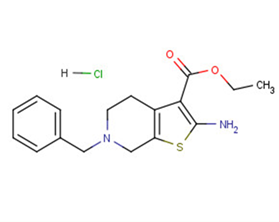
Tinoridine hydrochloride
CAS No. 25913-34-2
Tinoridine hydrochloride( Y-3642 hydrochloride )
Catalog No. M18320 CAS No. 25913-34-2
Tinoridine (Y-3642) is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Tinoridine (5-100 μM), produced a concentration-dependent inhibition on the simultaneous increases in lipid peroxide formation and renin release induced by 50 μM ascorbic acid in the renin granule fraction.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 85 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 76 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 122 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 217 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 305 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 461 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameTinoridine hydrochloride
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionTinoridine (Y-3642) is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Tinoridine (5-100 μM), produced a concentration-dependent inhibition on the simultaneous increases in lipid peroxide formation and renin release induced by 50 μM ascorbic acid in the renin granule fraction.
-
DescriptionTinoridine (Y-3642) is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Tinoridine (5-100 μM), produced a concentration-dependent inhibition on the simultaneous increases in lipid peroxide formation and renin release induced by 50 μM ascorbic acid in the renin granule fraction. On the other hand, indomethacin, hydrocortisone, and prednisolone, which had no ability to inhibit the lipid peroxidation in the renin granule fraction, did not influence the release of renin from the granules. These results suggest that tinoridine suppresses renin release by inhibiting the oxidative disintegration of membranes of renin granules.(In Vitro):Tinoridine reduces a stable free radical, diphenyl-p-picrylhydrazyl, in the molar ratio of about 1:2, indicating its free radical scavenging ability. Tinoridine inhibits the lipid peroxidation in rat liver microsomes induced by xanthine-xanthine oxidase system in the presence of ADP and Fe2+, in which hydroxyl radical is formed. Tinoridine is demonstrated to be oxidized in the course of the lipid peroxidation by following the fluorescence derived from the oxidation product of tinoridine. It is also oxidized by the xanthine-xanthine oxidase system in the presence of Fe2+, but its oxidation is slow in the absence of Fe2+ and almost completely inhibited by catalase. Tinoridine is also oxidized by H2O2-Fe2+ system producing OH (Fenton reaction), but it does not affect the reduction of cytochrome c caused by superoxide radical.(In Vivo):CCl4 aministration produces a marked decrease in the concentrations of liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 and G6Pase, indicating that hepatic endoplasmic reticulum function is disrupted. Prior treatment of the animals with tinoridine (100 mg/kg) significantly reduces the CCl4-induced alterations in the enzyme activities, and a rapid recovery toward the normal values is observed.
-
In VitroTinoridine reduces a stable free radical, diphenyl-p-picrylhydrazyl, in the molar ratio of about 1:2, indicating its free radical scavenging ability. Tinoridine inhibits the lipid peroxidation in rat liver microsomes induced by xanthine-xanthine oxidase system in the presence of ADP and Fe2+, in which hydroxyl radical is formed. Tinoridine is demonstrated to be oxidized in the course of the lipid peroxidation by following the fluorescence derived from the oxidation product of tinoridine. It is also oxidized by the xanthine-xanthine oxidase system in the presence of Fe2+, but its oxidation is slow in the absence of Fe2+ and almost completely inhibited by catalase. Tinoridine is also oxidized by H2O2-Fe2+ system producing OH (Fenton reaction), but it does not affect the reduction of cytochrome c caused by superoxide radical.
-
In VivoCCl4 aministration produces a marked decrease in the concentrations of liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 and G6Pase, indicating that hepatic endoplasmic reticulum function is disrupted. Prior treatment of the animals with tinoridine (100 mg/kg) significantly reduces the CCl4-induced alterations in the enzyme activities, and a rapid recovery toward the normal values is observed.
-
SynonymsY-3642 hydrochloride
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorCOX
-
Research AreaInflammation/Immunology
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number25913-34-2
-
Formula Weight352.88
-
Molecular FormulaC17H21ClN2O2S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : ≥ 31 mg/mL; 87.85 mM
-
SMILESO=C(C1=C(N)SC2=C1CCN(CC3=CC=CC=C3)C2)OCC.Cl
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Kalariya PD, etal. J Mass Spectrom. 2015 Nov;50(11):1222-33
molnova catalog



related products
-
Methoxyfenozide
Methoxyfenozide is an insect growth regulator. Methoxyfenozide used in the control of lepidopteran insect pests.
-
Senecioic acid
Senecioic acid appears in the urine of patients with 3-Methylcrotonic aciduria which is a disorder characterized by urine that contains increased amounts of 3-methylcrotonic acid (Senecioic acid).
-
Astressin
Astressin is an amino-terminal truncated analog of CRF that retains high affinity binding to the extracellular domain of the receptor and is believed to act as a neutral competitive antagonist of receptor activation.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


