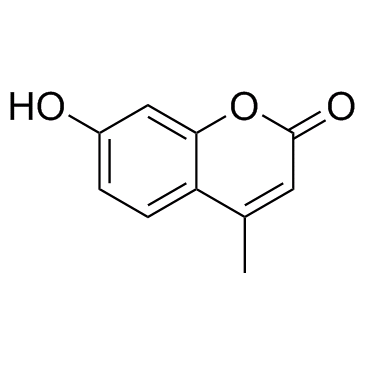
4-Methylumbelliferone
CAS No. 90-33-5
4-Methylumbelliferone ( 4-MU )
Catalog No. M16492 CAS No. 90-33-5
A coumarin derivative possessing properties as a spasmolytic, choleretic and light-protective agent.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 54 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 35 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 50 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name4-Methylumbelliferone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionA coumarin derivative possessing properties as a spasmolytic, choleretic and light-protective agent.
-
DescriptionA coumarin derivative possessing properties as a spasmolytic, choleretic and light-protective agent. It is also used in analytical chemistry techniques for the determination of Nitric acid.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms4-MU
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorASST
-
Research AreaOther Indications
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number90-33-5
-
Formula Weight176.17
-
Molecular FormulaC10H8O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityEthanol: 35 mg/mL (198.67 mM); DMSO: 35 mg/mL (198.67 mM)
-
SMILESO=C1C=C(C)C2=C(O1)C=C(O)C=C2
-
Chemical Name7-Hydroxy-4-methyl-2H-chromen-2-one
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Berman HM, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Pancreatic Polypepti...
Pancreatic Polypeptide (1-17)-(Ala31,Aib32)-Neuropeptide Y (18-36) (human)
-
8-Hydroxy Moxifloxac...
8-Hydroxy Moxifloxacin Hydrobromide
-
Adipokinetic Hormone...
Adipokinetic hormone II (Locusta migratoria) (Lom-AKH-II) is a insect adipokinetic hormone (AKH), enhances fat body cAMP levels in vitro. Insect adipokinetic hormones (AKHs) controls flight-directed mobilization of carbohydrate and lipid from fat body stores, which depends on AKH receptor(s) coupling to cAMP formation and glycogen phosphorylase activation via the stimulatory guanine nucleotide-binding protein (Gs).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


