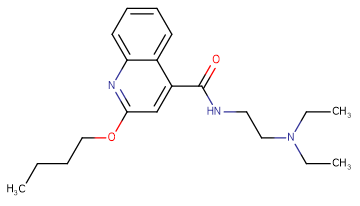
Dibucaine
CAS No. 85-79-0
Dibucaine( NSC 159055 )
Catalog No. M16224 CAS No. 85-79-0
Dibucaine is a local anesthetic of the amide type now generally used for surface anesthesia.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 46 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 41 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 48 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDibucaine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDibucaine is a local anesthetic of the amide type now generally used for surface anesthesia.
-
DescriptionDibucaine is a local anesthetic of the amide type now generally used for surface anesthesia.(In Vitro):Dibucaine (Cinchocaine) reduces the degradation of BSA-gold complex in the reservosomes, which was not caused either by an inhibition of the whole proteolytic activity of the parasite or by a reduction on the expression levels of cruzipain. Dibucaine, a quaternary ammonium compound, inhibited SChE to a minimum within 2 min in a reversible manner. The inhibition was very potent. It had an IC(50) of 5.3 microM with BuTch or 3.8 microM with AcTch. The inhibition was competitive with respect to BuTch with a K(i) of 1.3 microM and a linear-mixed type (competitive/noncompetitive) with respect to AcTch with inhibition constants, K(i) and K(I) of 0.66 and 2.5 microM, respectively. Dibucaine possesses a butoxy side chain that is similar to the butryl group of BuTch and longer by an ethylene group from AcTch.
-
In VitroDibucaine (Cinchocaine) reduces the degradation of BSA-gold complex in the reservosomes, which was not caused either by an inhibition of the whole proteolytic activity of the parasite or by a reduction on the expression levels of cruzipain.Dibucaine, a quaternary ammonium compound, inhibited SChE to a minimum within 2 min in a reversible manner. The inhibition was very potent. It had an IC(50) of 5.3 microM with BuTch or 3.8 microM with AcTch. The inhibition was competitive with respect to BuTch with a K(i) of 1.3 microM and a linear-mixed type (competitive/noncompetitive) with respect to AcTch with inhibition constants, K(i) and K(I) of 0.66 and 2.5 microM, respectively. Dibucaine possesses a butoxy side chain that is similar to the butryl group of BuTch and longer by an ethylene group from AcTch.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsNSC 159055
-
PathwayEndocrinology/Hormones
-
TargetAChR
-
RecptorAChR| CAM| Sodium Channel
-
Research AreaNeurological Disease
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number85-79-0
-
Formula Weight343.46
-
Molecular FormulaC20H29N3O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityWater: 42 mg/L (at 21 °C)
-
SMILESCCCCOC1=NC2=CC=CC=C2C(=C1)C(=O)NCCN(CC)CC
-
Chemical Name2-butoxy-N-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]quinoline-4-carboxamide
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Oka M, et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002 Oct 4;452(2):175-8
molnova catalog



related products
-
N-p-trans-Coumaroylt...
N-p-trans-Coumaroyltyramine is a natural product, is an acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor with an an IC50 of 122 μM.?N-p-trans-Coumaroyltyramine exhibits anti-trypanosomal activity with an IC50 of 13.3 μM for T. brucei rhodesiense.
-
Questin
Questin is an antibacterial agent isolated from marine Aspergillus flavipes. Questin exhibits antibacterial activity against V. harveyi, V. anguillarum, V. cholerae, and V. parahemolyticus with MIC values of 31.25 μg/mL, 62.5 μg/mL, 62.5 μg/mL, and 125 μg/mL.
-
Pregnenolone
A 21-carbon steroid, derived from CHOLESTEROL and found in steroid hormone-producing tissues.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


