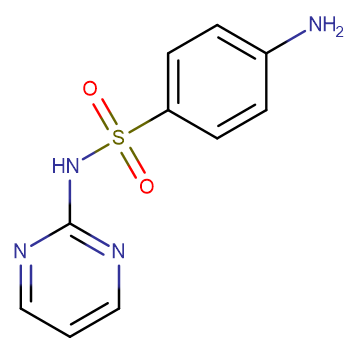
Sulfadiazine
CAS No. 68-35-9
Sulfadiazine( NSC 35600 )
Catalog No. M15612 CAS No. 68-35-9
Sulfadiazine is a sulfonamide antibiotic. It eliminates bacteria that cause infections by stopping the production of folic acid inside the bacterial cell, and is commonly used to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 37 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSulfadiazine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSulfadiazine is a sulfonamide antibiotic. It eliminates bacteria that cause infections by stopping the production of folic acid inside the bacterial cell, and is commonly used to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs).
-
DescriptionSulfadiazine is a sulfonamide antibiotic. It eliminates bacteria that cause infections by stopping the production of folic acid inside the bacterial cell, and is commonly used to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs). In combination, sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine, can be used to treat toxoplasmosis, a disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii.(In Vitro):In this study, the effectiveness of Sulfadiazine and Pyrimetamine for the treatment of mice during acute infection with different atypical T. gondii strains was evaluated. Swiss mice were infected with seven T. gondii strainsl. The infected mice were treated with 10-640 mg/kg per day of Sulfadiazine, 3-200 mg/kg per day of Pyrimetamine, or a combination of both drugs with a lower dosage. A descriptive analysis was used to assess the association between susceptibility to Sulfadiazine and/or Pyrimetamine and the genotype. The TgCTBr4 and TgCTBr17 strains (genotype 108) presented lower susceptibility to Sulfadiazine or Pyrimetamine treatment. The TgCTBr1 and TgCTBr25 strains (genotype 206) presented similar susceptibility to PYR but not Sulfadiazine treatment. The TgCTBr9 strain (genotype 11) was the only strain with high susceptibility to treatment with both drugs.
-
In Vitro——
-
In VivoIn this study, the effectiveness of Sulfadiazine and Pyrimetamine for the treatment of mice during acute infection with different atypical T. gondii strains was evaluated. Swiss mice were infected with seven T. gondii strainsl. The infected mice were treated with 10-640?mg/kg per day of Sulfadiazine, 3-200?mg/kg per day of Pyrimetamine, or a combination of both drugs with a lower dosage. A descriptive analysis was used to assess the association between susceptibility to Sulfadiazine and/or Pyrimetamine and the genotype. The TgCTBr4 and TgCTBr17 strains (genotype 108) presented lower susceptibility to Sulfadiazine or Pyrimetamine treatment. The TgCTBr1 and TgCTBr25 strains (genotype 206) presented similar susceptibility to PYR but not Sulfadiazine treatment. The TgCTBr9 strain (genotype 11) was the only strain with high susceptibility to treatment with both drugs.
-
SynonymsNSC 35600
-
PathwayAutophagy
-
TargetAutophagy
-
RecptorDHPS
-
Research AreaInfection
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number68-35-9
-
Formula Weight250.28
-
Molecular FormulaC10H10N4O2S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 50 mg/mL (199.77 mM)
-
SMILESO=S(NC1=NC=CC=N1)(C2=CC=C(N)C=C2)=O
-
Chemical Name4-amino-N-(pyrimidin-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Iliades P, et al. Antimicrob Agents ChemOthers. 2005 Feb;49(2):741-8.
molnova catalog



related products
-
GSK4112
A potent and selective small molecule Rev-erbα agonist with EC50 of 0.4 uM in biochemical assay.
-
AUTEN-99 hydrobromid...
A small molecule autophagy enhancer that inhibit the myotubularin-related phosphatase MTMR14/Jumpy.
-
Hemin
Hemin, a physiological erythroid maturation stimulator, is able to induce the expression of critical autophagic genes (Map1a1b (LC3), Beclin-1 gen, Atg5) in an erythroleukemia cell type.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


