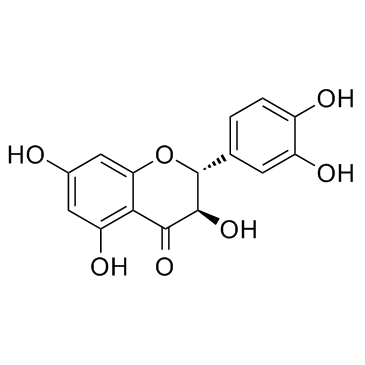
Taxifolin (Dihydroquercetin)
CAS No. 480-18-2
Taxifolin (Dihydroquercetin)( (+)-Dihydroquercetin )
Catalog No. M14601 CAS No. 480-18-2
Taxifolin is a flavonoid in many plants such as Taxus chinensis, Siberian larch, Cedrus deodara and so on.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 41 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 66 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameTaxifolin (Dihydroquercetin)
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionTaxifolin is a flavonoid in many plants such as Taxus chinensis, Siberian larch, Cedrus deodara and so on.
-
DescriptionTaxifolin is a flavonoid in many plants such as Taxus chinensis, Siberian larch, Cedrus deodara and so on.(In Vitro):This is confirmed by the investigation of pure Taxifolin and (+)-Catechin against collagenase activity. Taxifolin exhibits significant inhibitory activity with an IC50 value of 193.3 μM while (+)-Catechin is not active. Taxifolin is a ubiquitous bioactive constituent of foods and herbs. Taxifolin (dihydroquercetin) is a bioactive flavanonol commonly found in grapes, citrus fruits, onions, green tea, olive oil, wine, and many other foods, as well as several herbs (such as milk thistle, French maritime bark, Douglas fir bark, and Smilacis Glabrae Rhizoma).(In Vivo):Taxifolin may be easily metabolized and that its metabolites are the prevalent form in vivo, although limited information is available on metabolism of Taxifolin in vivo.
-
In VitroThis is confirmed by the investigation of pure Taxifolin and (+)-Catechin against collagenase activity. Taxifolin exhibits significant inhibitory activity with an IC50 value of 193.3 μM while (+)-Catechin is not active. Taxifolin is a ubiquitous bioactive constituent of foods and herbs. Taxifolin (dihydroquercetin) is a bioactive flavanonol commonly found in grapes, citrus fruits, onions, green tea, olive oil, wine, and many other foods, as well as several herbs (such as milk thistle, French maritime bark, Douglas fir bark, and Smilacis Glabrae Rhizoma).
-
In VivoTaxifolin may be easily metabolized and that its metabolites are the prevalent form in vivo, although limited information is available on metabolism of Taxifolin in vivo.
-
Synonyms(+)-Dihydroquercetin
-
PathwayEndocrinology/Hormones
-
TargetAdrenergic Receptor
-
Recptorβ-adrenergic receptor| TNF-α| Collagenase Tyrosinase| Beta-nerve growth factor| VEGFR2
-
Research AreaMetabolic Disease
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number480-18-2
-
Formula Weight304.25
-
Molecular FormulaC15H12O7
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityEthanol: 60 mg/mL (197.2 mM); DMSO: 60 mg/mL (197.2 mM)
-
SMILESO=C1[C@H](O)[C@@H](C2=CC=C(O)C(O)=C2)OC3=CC(O)=CC(O)=C13
-
Chemical Name(2R,3R)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxychroman-4-one
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Makena PS, et al. Environ Mol Mutagen, 2009, 50(6), 451-459.
molnova catalog



related products
-
(±)-Bisoprolol hemif...
Bisoprolol is a selective type β1 adrenergic receptor blocker.
-
Formoterol
Formoterol is a novel highly β2-selective adrenergic agonist and holds promise as a β2-agonist that could impart selective beneficial metabolic effects.
-
Armodafinil
Armodafinil(CRL 40982; CEP 10952) is an enantiopure drug consisting of just the active (-)-(R)-enantiomer of the racemic drug modafinil (Provigil).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


