Curcumin
CAS No. 458-37-7
Curcumin( Indian Saffron | Turmeric yellow )
Catalog No. M14544 CAS No. 458-37-7
Curcumin is a natural phenolic compound with impressive antioxidant properties. Curcumin is recently proved to exert its chemopreventive effects partly through the activation of nuclear factor (erythroid-2 related) factor 2 (Nrf2).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 48 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 34 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 47 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 80 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 110 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCurcumin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCurcumin is a natural phenolic compound with impressive antioxidant properties. Curcumin is recently proved to exert its chemopreventive effects partly through the activation of nuclear factor (erythroid-2 related) factor 2 (Nrf2).
-
DescriptionCurcumin is a natural phenolic compound with impressive antioxidant properties. Curcumin is recently proved to exert its chemopreventive effects partly through the activation of nuclear factor (erythroid-2 related) factor 2 (Nrf2).(In Vitro):Curcumin exerts its chemopreventive effects partly through the activation of nuclear factor (erythroid-2 related) factor 2 (Nrf2) and its antioxidant and phase II detoxifying enzymes. Curcumin inhibits T47D cells growth, with IC50s of 25, 19 and 17.5 μM for 24, 48 and 72 h MTT assays respectively. IC50s of curcumin and silibinin mixture against T47D cells, are 17.5, 15, and 12 μM for 24, 48, and 72 h exposure times, respectively. Curcumin (2.5-80 μM) induces apoptotic cell death in AGS and HT-29 cell lines, and the IC50 is 21.9±0.1, 40.7±0.5 μM, respectively, in both AGS and HT-29 cell lines. Curcumin-induced apoptosis requires caspase activities in AGS and HT-29 cells. Curcumin induces ER Ca2+ decline and mitochondrial Ca2+ overloading. Curcumin induces the G2/M cell cycle arrest of LNCaP and PC-3 cells in a dose dependent manner. Curcumin upregulates the protein level of NF-kappaB inhibitor IkappaBalpha and downregulates protein levels of c-Jun and AR. (In Vivo):Curcumin (10 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly prevents decrease in the percentage of sucrose consumption, as compared to the CMS-exposed rats. Curcumin treatment results in significant prevention of increase in TNF-α and IL-6 levels in stressed rats. Curcumin decreases binding of p300/CREB-binding protein (CBP) at the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) promoter at 20 mg/kg (i.p.), reduces binding of P300/CBP at the BDNF promoter at 40 mg/kg, and decreases binding all the four proteins of p300/CBP and H3K9ac/H4K5ac at the BDNF promoter at 60 mg/kg in chronic constriction injury (CCI) rats.
-
In VitroCurcumin exerts its chemopreventive effects partly through the activation of nuclear factor (erythroid-2 related) factor 2 (Nrf2) and its antioxidant and phase II detoxifying enzymes. Curcumin inhibits T47D cells growth, with IC50s of 25, 19 and 17.5 μM for 24, 48 and 72 h MTT assays respectively. IC50s of curcumin and silibinin mixture against T47D cells, are 17.5, 15, and 12 μM for 24, 48, and 72 h exposure times, respectively. Curcumin (2.5-80 μM) induces apoptotic cell death in AGS and HT-29 cell lines, and the IC50 is 21.9±0.1, 40.7±0.5 μM, respectively, in both AGS and HT-29 cell lines. Curcumin-induced apoptosis requires caspase activities in AGS and HT-29 cells. Curcumin induces ER Ca2+ decline and mitochondrial Ca2+ overloading. Curcumin induces the G2/M cell cycle arrest of LNCaP and PC-3 cells in a dose dependent manner. Curcumin upregulates the protein level of NF-kappaB inhibitor IkappaBalpha and downregulates protein levels of c-Jun and AR.
-
In VivoCurcumin (10 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly prevents decrease in the percentage of sucrose consumption, as compared to the CMS-exposed rats. Curcumin treatment results in significant prevention of increase in TNF-α and IL-6 levels in stressed rats. Curcumin decreases binding of p300/CREB-binding protein (CBP) at the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) promoter at 20 mg/kg (i.p.), reduces binding of P300/CBP at the BDNF promoter at 40 mg/kg, and decreases binding all the four proteins of p300/CBP and H3K9ac/H4K5ac at the BDNF promoter at 60 mg/kg in chronic constriction injury (CCI) rats.
-
SynonymsIndian Saffron | Turmeric yellow
-
PathwayChromatin/Epigenetic
-
TargetEpigenetic Reader Domain
-
Recptorp300 histone acetylatransferase| KEAP1-Nrf2
-
Research AreaOther Indications
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number458-37-7
-
Formula Weight368.39
-
Molecular FormulaC21H20O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 73mg/ml (198.16 mM); Water: <1mg/ml; Ethanol: <1mg/ml
-
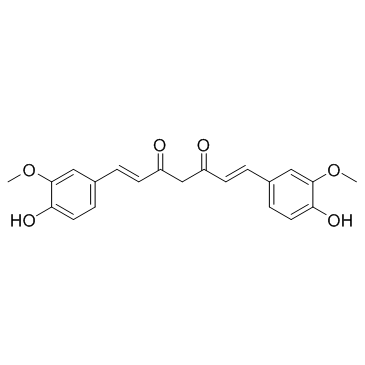
SMILESO=C(CC(/C=C/C1=CC=C(O)C(OC)=C1)=O)/C=C/C2=CC=C(O)C(OC)=C2
-
Chemical Name(1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Zanotto-Filho A, et al. Y Lett. 2015 Mar 28;358(2):220-3
molnova catalog



related products
-
BRD4-BD1-IN-2
BRD4-BD1-IN-2 is a selective and potent BRD4-BD1 inhibitor with an IC50 value of 2.51 μM, exhibiting 20-fold greater inhibitory activity against BRD4-BD1 compared to BRD4-BD2.
-
Diflunisal
Diflunisal, a salicylate derivative, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent (NSAIA) with pharmacologic actions similar to other prototypical NSAIAs.
-
CTB
CTB (Cholera Toxin B subunit) is an activator of p300 histone acetyltransferase and induces apoptosis in MCF-7 cells.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


