6-FABA
CAS No. 434-76-4
6-FABA( 6-Fluoroanthranilic Acid )
Catalog No. M14483 CAS No. 434-76-4
6-FABA (6-Fluoroanthranilic Acid) is a small-molecule inhibitor of MTB tryptophan synthesis that converts Mtb into a tryptophan auxotroph and restores the efficacy of a failed host defense.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | 27 | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name6-FABA
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description6-FABA (6-Fluoroanthranilic Acid) is a small-molecule inhibitor of MTB tryptophan synthesis that converts Mtb into a tryptophan auxotroph and restores the efficacy of a failed host defense.
-
Description6-FABA (6-Fluoroanthranilic Acid) is a small-molecule inhibitor of MTB tryptophan synthesis that converts Mtb into a tryptophan auxotroph and restores the efficacy of a failed host defense; has an MIC of 5 uM in liquid broth in the absence of tryptophan in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms6-Fluoroanthranilic Acid
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetAntibacterial
-
RecptorAntibacterial
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number434-76-4
-
Formula Weight155.13
-
Molecular FormulaC7H6FNO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (644.62 mM)
-
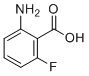
SMILESC1=CC(=C(C(=C1)F)C(=O)O)N
-
Chemical Name2-Amino-6-fluorobenzoic acid
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Zhang YJ, et al. Cell. 2013 Dec 5;155(6):1296-308.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Fidaxomicin
Fidaxomicin(OPT-80; PAR-101) is a?new class of narrow spectrum macrocyclic antibiotic drug.
-
Cefamandole nafate
Cefamandole nafate is a second-generation broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic.
-
N-(3-cyano-4,5,6,7-t...
N-(3-cyano-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1-benzothiophen-2-yl)pyrazine-2-carboxamide exhibit an inhibitory effect on bacterial DNA helicases, nucleases, or helicase-nuclease enzyme complexes, such as, for example, one or more enzymes selected from the RecBCD and AddAB families of enzymes.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


