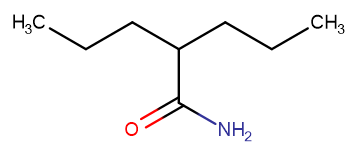
Valpramide
CAS No. 2430-27-5
Valpramide( Valpromide | Depamide )
Catalog No. M13702 CAS No. 2430-27-5
Valpromide is a carboxamide derivative of valproic acid used in the treatment of epilepsy and some affective disorders.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 29 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 41 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 91 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 138 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameValpramide
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionValpromide is a carboxamide derivative of valproic acid used in the treatment of epilepsy and some affective disorders.
-
DescriptionValpromide is a carboxamide derivative of valproic acid used in the treatment of epilepsy and some affective disorders.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsValpromide | Depamide
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor2-epoxide hydrolase| Limonene-1
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2430-27-5
-
Formula Weight143.23
-
Molecular FormulaC8H17NO
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 10 mM
-
SMILESCCCC(CCC)C(N)=O
-
Chemical Name2-propylpentanamide
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Lemoine P, et al. Eur Psychiatry. 2000 Nov;15(7):424-32.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Mast Cell Degranulat...
Peptide from giant hornet Vespa orientalis that has biological effects similar to mast cell degranulating peptide from bee venom.
-
Trametenolic acid
Trametenolic acid is a cytotoxic agent.It exhibits a mode of mixed inhibition with a K I of 0.9μM, K IS of 0.5μM, and an IC50 of 7.25μM.
-
Adenosine-5'-diphosp...
Adenosine 5'-diphosphate sodium salt is an adenine nucleotide that is phosphorylated into ATP by ATPase. This phosphorylation is a key part of cellular homeostatis as it allows for energy storage and is involved in nucleic acid metabolism. ADP affects platelet activation through its interaction with ADP receptors P2Y1 P2Y12 and P2X1.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


