HIV-1 Integrase Inhibitor 1
CAS No. 2146094-22-4
HIV-1 Integrase Inhibitor 1( —— )
Catalog No. M13429 CAS No. 2146094-22-4
A novel compound that disrupts the HIV-1 integrase LEDGF interaction.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameHIV-1 Integrase Inhibitor 1
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionA novel compound that disrupts the HIV-1 integrase LEDGF interaction.
-
DescriptionA novel compound that disrupts the HIV-1 integrase LEDGF interaction; produces an ALLINI-like phenotype through engagement of IN sites distinct from the LEDGF pocket.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayMicrobiology/Virology
-
TargetHIV
-
RecptorHIV
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2146094-22-4
-
Formula Weight480.579
-
Molecular FormulaC26H28N2O5S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
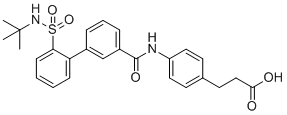
SMILESCC(C)(C)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1C2=CC(=CC=C2)C(=O)NC3=CC=C(C=C3)CCC(=O)O
-
Chemical Name3-(4-(2'-(N-(tert-butyl)sulfamoyl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-3-carboxamido)phenyl)propanoic acid
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Burlein C, et al. ACS Chem Biol. 2017 Nov 17;12(11):2858-2865.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Atazanavir sulfate
A highly potent HIV-1 protease inhibitor that exhibits potent anti-HIV activity EC50 of 2.6-5.3 nM and EC90 of 9-15 nM in cell culture.
-
NBD-11021
A small molecule, full antagonist of CD4 that blocks gp120-CD4 interaction.
-
Escin IA;Aescin IA
Escin IA is a triterpene saponin isolated from horse chestnut which inhibits HIV-1 protease with IC50 values of 35 μM. Escin IA has anti-TNBC metastasis activity and its action mechanisms involved inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition process by down-regulating LOXL2 expression.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


