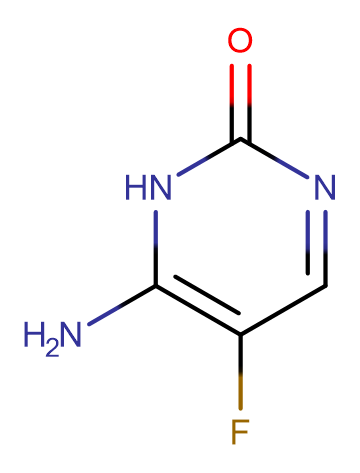
Fluorocytosine
CAS No. 2022-85-7
Fluorocytosine( Ancobon | Ancotil | 5-FC | NSC 103805 | Ro 2-9915 )
Catalog No. M13149 CAS No. 2022-85-7
Flucytosine is a Nucleoside Analog Antifungal. The chemical classification of flucytosine is Nucleoside Analog.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 46 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 33 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 45 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameFluorocytosine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionFlucytosine is a Nucleoside Analog Antifungal. The chemical classification of flucytosine is Nucleoside Analog.
-
DescriptionFlucytosine is a Nucleoside Analog Antifungal. The chemical classification of flucytosine is Nucleoside Analog.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsAncobon | Ancotil | 5-FC | NSC 103805 | Ro 2-9915
-
PathwayCell Cycle/DNA Damage
-
TargetDNA/RNA Synthesis
-
RecptorDNA synthesis
-
Research AreaInfection
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2022-85-7
-
Formula Weight129.09
-
Molecular FormulaC4H4FN3O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityWater: 5 mg/mL (38.73 mM); DMSO: 8 mg/mL (61.97 mM)
-
SMILESO=C1N=CC(F)=C(N)N1
-
Chemical Name6-amino-5-fluoro-1H-pyrimidin-2-one
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Osterman DG, et al. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):5204-10.
molnova catalog



related products
-
TFMB-(S)-2-HG
TFMB-(S)-2-HG (TFMB S 2 HG) is a highly effective inhibitor of TET2, the 5'-methylcytosine hydroxylase. Additionally, it significantly inhibits the EglN prolyl hydroxylases.
-
Gentisin
Gentisin is a novel inhibitor of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) proliferation with an IC50 value of 7.84 μM. Gentisin has mutagenic activity.
-
NCGC00029283
NCGC00029283 is a potent inhibitor of Werner syndrome helicase-nuclease (WRN), displaying inhibitory activity against WRN helicase with an IC 50 value of 2.3 μM.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


