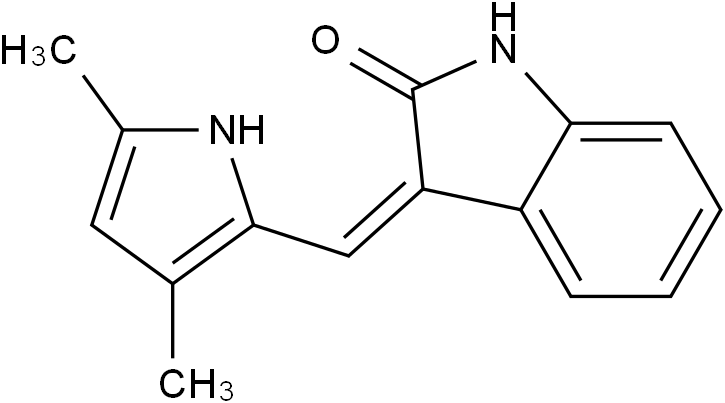
Semaxanib
CAS No. 194413-58-6
Semaxanib ( SU5416 )
Catalog No. M13045 CAS No. 194413-58-6
Semaxanib (SU5416) is a potent and selective VEGFR(Flk-1/KDR) inhibitor with IC50 of 1.23 μM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 30 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 48 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 71 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 111 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 174 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 341 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSemaxanib
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSemaxanib (SU5416) is a potent and selective VEGFR(Flk-1/KDR) inhibitor with IC50 of 1.23 μM.
-
DescriptionSemaxanib (SU5416) is a potent and selective VEGFR(Flk-1/KDR) inhibitor with IC50 of 1.23 μM, 20-fold more selective for VEGFR than PDGFRβ, lack of activity against EGFR, InsR and FGFR. Phase 3.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsSU5416
-
PathwayAngiogenesis
-
TargetVEGFR
-
RecptorVEGFR2/Flk1
-
Research AreaCancer
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number194413-58-6
-
Formula Weight238.28
-
Molecular FormulaC15H14N2O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityEthanol: 2 mg/mL (8.39 mM); DMSO: 22 mg/mL (92.32 mM)
-
SMILESCC1=CC(=C(N1)/C=C\2/C3=CC=CC=C3NC2=O)C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Fong TA, et al. Y Res, 1999, 59(1), 99-106.
molnova catalog



related products
-
TG 100801
TG 100801 is a dual inhibitor of VEGFr2 and Src family (Src and YES) kinases and is a candidate compound for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
-
Jaceidin
Jaceidin is a membrane-permeable inhibitor of VEGFR with anti-tumor activities.
-
GSK269962A
GSK269962 is a selective ROCK(Rho-associated protein kinase) inhibitor with IC50 values of 1.6 and 4 nM for ROCK1 and ROCK2, respectively.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


