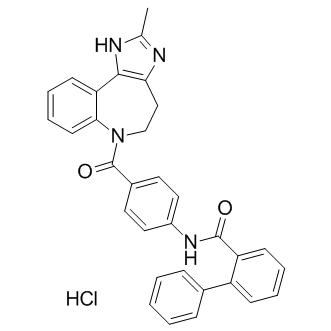
Conivaptan hydrochloride
CAS No. 168626-94-6
Conivaptan hydrochloride( YM-087 )
Catalog No. M12574 CAS No. 168626-94-6
Conivaptan (YM-087) is a potent, selective nonpeptide vasopressin V1A and V2 receptor antagonist with Ki of 0.48 nM and 3.04 nM respectively.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 33 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 53 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 119 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 214 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 357 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | 537 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameConivaptan hydrochloride
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionConivaptan (YM-087) is a potent, selective nonpeptide vasopressin V1A and V2 receptor antagonist with Ki of 0.48 nM and 3.04 nM respectively.
-
DescriptionConivaptan (YM-087) is a potent, selective nonpeptide vasopressin V1A and V2 receptor antagonist with Ki of 0.48 nM and 3.04 nM respectively; less potent for OT receptors and no effect on V1B receptor; blocks AVP-induced cAMP production of cultured renal epithelium cells concentration dependently and has no agonistic activities.Other Indication Approved(In Vivo):Conivaptan (0.03, 0.1 and 0.3 mg/kg, i.v.) dose-dependently increases urine volume and reduces urine osmolality in both myocardial infarction and sham-operated rats. Conivaptan (0.3 mg/kg i.v.) significantly reduces right ventricular systolic pressure, left ventricular end-diastolic pressure, lung/body weight and right atrial pressure in myocardial infarction rats. Conivaptan (0.3 mg/kg i.v.) significantly increases dP/dt(max)/left ventricular pressure in myocardial infarction rats. Conivaptan produces an acute increase in urine volume (UV), a reduction in osmolality (UOsm) and, at the end of the investigation, cirrhotic rats receiving the V(1a)/V(2)-AVP receptor antagonist does not show hyponatremia or hypoosmolality. Conivaptan also normalizes U(Na)V without affecting creatinine clearance and arterial pressure. Conivaptan (0.01 to 0.1 mg/kg, i.v.) exerts a dose-dependent diuretic effect in dogs without an increase in the urinary excretion of electrolytes, inhibits the pressor effect of exogenous vasopressin in a dose-dependent manner (0.003 to 0.1 mg/kg i.v.) and, at the highest dose (0.1 mg/kg i.v.), almost completely blocks vasoconstriction caused by exogenous vasopressin. Conivaptan (0.1 mg/kg, i.v.) improves cardiac function, as evidenced by significant increases in left ventricular dP/dtmax, cardiac output and stroke volume, and reduces preload and afterload, as evidenced by significant decreases in left ventricular end-diastolic pressure and total peripheral vascular resistance in dogs with congestive heart failure.
-
In Vitro——
-
In VivoConivaptan (0.03, 0.1 and 0.3 mg/kg, i.v.) dose-dependently increases urine volume and reduces urine osmolality in both myocardial infarction and sham-operated rats. Conivaptan (0.3 mg/kg i.v.) significantly reduces right ventricular systolic pressure, left ventricular end-diastolic pressure, lung/body weight and right atrial pressure in myocardial infarction rats. Conivaptan (0.3 mg/kg i.v.) significantly increases dP/dt(max)/left ventricular pressure in myocardial infarction rats. Conivaptan produces an acute increase in urine volume (UV), a reduction in osmolality (UOsm) and, at the end of the investigation, cirrhotic rats receiving the V(1a)/V(2)-AVP receptor antagonist does not show hyponatremia or hypoosmolality. Conivaptan also normalizes U(Na)V without affecting creatinine clearance and arterial pressure. Conivaptan (0.01 to 0.1 mg/kg, i.v.) exerts a dose-dependent diuretic effect in dogs without an increase in the urinary excretion of electrolytes, inhibits the pressor effect of exogenous vasopressin in a dose-dependent manner (0.003 to 0.1 mg/kg i.v.) and, at the highest dose (0.1 mg/kg i.v.), almost completely blocks vasoconstriction caused by exogenous vasopressin. Conivaptan (0.1 mg/kg, i.v.) improves cardiac function, as evidenced by significant increases in left ventricular dP/dtmax, cardiac output and stroke volume, and reduces preload and afterload, as evidenced by significant decreases in left ventricular end-diastolic pressure and total peripheral vascular resistance in dogs with congestive heart failure.
-
SynonymsYM-087
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetVasopressin Receptor
-
Recptorvasopressinreceptor1a|vasopressinreceptor2
-
Research AreaOther Indications
-
IndicationOther Disease
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number168626-94-6
-
Formula Weight535.0354
-
Molecular FormulaC32H27ClN4O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility10 mM in DMSO
-
SMILESO=C(NC1=CC=C(C(N2CCC(NC(C)=N3)=C3C4=CC=CC=C42)=O)C=C1)C5=CC=CC=C5C6=CC=CC=C6.[H]Cl
-
Chemical Name[1,1'-Biphenyl]-2-carboxamide, N-[4-[(4,5-dihydro-2-methylimidazo[4,5-d][1]benzazepin-6(1H)-yl)carbonyl]phenyl]-, hydrochloride (1:1)
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
d[Leu4,Lys8]-VP
Selective vasopressin V1B receptor agonist (Ki values are 0.16, 64, 100 and 3800 nM for V1B, oxytocin, V2 and V1A receptors respectively). Displays weak antidiuretic, vasopressor and in vitro oxytocic activities.
-
Tolvaptan
Tolvaptan (OPC-41061) is a highly potent selective, competitive vasopressin V2-receptor antagonist with Ki of 0.43 nM.
-
(d(CH2)51,Tyr(Me)2,A...
Selective vasopressin V1A receptor antagonist. Inhibits vasopressin and oxytocin-induced increases in intracellular calcium concentrations in vitro (IC50 values are 5 and 30 nM respectively). Exhibits potent and prolonged antivasopressor activity and induces anxiolytic-like effects in the dorsal, but not ventral, hippocampus in vivo.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


