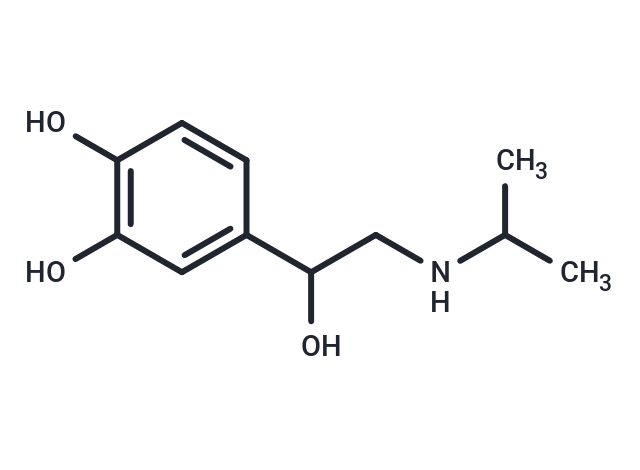
Isoproterenol
CAS No. 7683-59-2
Isoproterenol( —— )
Catalog No. M33728 CAS No. 7683-59-2
Isoproterenol (Norisodrine) is a non-selective and orally active β-adrenoceptor agonist.Isoproterenol is a potent peripheral vasodilator and bronchodilator.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 532 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 787 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 1074 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 1463 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 1960 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameIsoproterenol
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionIsoproterenol (Norisodrine) is a non-selective and orally active β-adrenoceptor agonist.Isoproterenol is a potent peripheral vasodilator and bronchodilator.
-
DescriptionIsoprenaline is a non-selective, orally active β-adrenergic receptor agonist. Isoprenaline has potent peripheral vasodilator, bronchodilator, and cardiac stimulating activities. Isoprenaline can be used for the research of bradycardia and bronchial asthma.
-
In VitroIsoprenaline (300 nM, 3 min) increases particulate cGMP- and cilostamide-inhibited, low-Km cAMP phosphodiesterase (cAMP-PDE) activity by about 100% in intact rat fat cells. Isoprenaline inhibits insulin-stimulated glucose transport activity in rat adipocytes. Isoprenaline, in the absence of adenosine, promotes a time-dependent (t1/2 approximately 2 min) decrease in the accessibility of insulin-stimulated cell surface GLUT4 of > 50%, which directly correlated with the observed inhibition of transport activity.Isoprenaline (5 nM and 10 μM) increases cyclic AMP levels and this effect is potentiated by cilostamide (10 mM), by rolipram, a cyclic AMP-specific PDE (PDE 4) inhibitor (10 mM) and by cyclic GMP-elevating agents (50 nM ANF or 30 nM SNP plus 100 nM DMPPO).Isoprenaline increases the transcriptional activity of Gi alpha-2 gene to 140% of the control value, whereas gene specific hybridization for Gs alpha remains unchanged. Isoprenaline (20 nM) increases the amplitude of total iK and causes a negative shift of approximately 10 mV in the activation curve for iK, both in the absence and in the presence of 300 nM nisoldipine to block the L-type Ca2+ current.Isoprenaline (20 nM) increases the spontaneous pacemaker rate of sino-atrial node pacemaker cells by 16% in rabbit isolated pacemaker cells.
-
In VivoIsoprenaline (oral, 0.27-0. 64 μg/kg) is extensively metabolizes by a relatively small number of reactions in dogs.Animal Model:Dogs Dosage:0.27-0. 64 μg/kg Administration:oral Result:Excreted largely unchanged in urine, only one-third of the radioactivity in urine was in the form of the O-methyl metabolite.Showed plasma radioactivity was almost entirely as conjugated isoprenaline and this metabolite accounted for more than 80% of radioactivity in urine.Showed heart rate returned to base-line values when high plasma concentrations.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite | Adrenergic Receptor
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number7683-59-2
-
Formula Weight211.26
-
Molecular FormulaC11H17NO3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESC(CNC(C)C)(O)C1=CC(O)=C(O)C=C1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Degerman E, et al. Evidence that insulin and isoprenaline activate the cGMP-inhibited low-Km cAMP phosphodiesterase in rat fat cells by phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):533-7.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
Tuftsin diacetate
Tuftsin diacetate, a tetrapeptide, is a macrophage/microglial activator. Tuftsin is a tetrapeptide, Thr-Lys-Pro-Arg, which resides in the Fc-domain of the heavy chain of immunoglobulin G. Tuftsin possesses a broad spectrum of activities related primarily to the immune system function and exerts on phagocytic cells, notably on macrophages.
-
34-Dihydroxyphenylac...
34-Dihydroxybenzeneacetic acid is the main neuronal metabolite of dopamine.
-
Tuftsin 3TFA
Tuftsin 3TFA is a tetrapeptide. It is a macrophage/microglial activator.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


