Flutriafol
CAS No. 76674-21-0
Flutriafol( —— )
Catalog No. M21161 CAS No. 76674-21-0
Flutriafol is a pesticide demethylation inhibitor and NMDA receptor agonist.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | 35 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 50 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 68 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | 88 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 168 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameFlutriafol
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionFlutriafol is a pesticide demethylation inhibitor and NMDA receptor agonist.
-
DescriptionFlutriafol is a pesticide demethylation inhibitor and NMDA receptor agonist.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayMembrane Transporter/Ion Channel
-
TargetNMDAR
-
RecptorNMDA receptor
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number76674-21-0
-
Formula Weight301.29
-
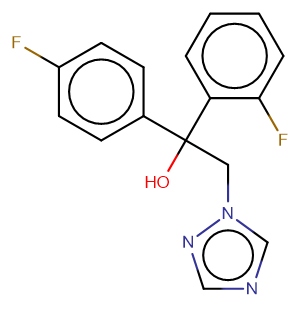
Molecular FormulaC16H13F2N3O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 250 mg/mL (829.77 mM)
-
SMILESOC(Cn1cncn1)(c1ccc(F)cc1)c1ccccc1F
-
Chemical Name1-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-(1H-124-triazol-1-yl)ethan-1-ol
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Zhang Q Hua X Yang Y et al. Stereoselective degradation of flutriafol and tebuconazole in grape[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research 2015 22(6):4350-4358.
molnova catalog



related products
-
DQP 1105
DQP 1105 is an NMDA receptor antagonist inhibiting receptor function more potently with glutamate.
-
(-)-MK-801 Maleate
(+)-MK-801?is a potent, selective and non-competitive?NMDA?receptor antagonist with?Kd?of 37.2 nM in rat brain membranes.
-
Ro 8-4304 Hydrochlor...
Ro 8-4304 Hydrochloride is an antagonist of NMDA receptor with IC50 of 0.4 μM?Ro 8-4304 is a voltage-independent, non-competitive antagonist of NMDA receptors in rat cultured cortical neurones and exhibits a state-dependent mode of action similar to that described for ifenprodil.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


