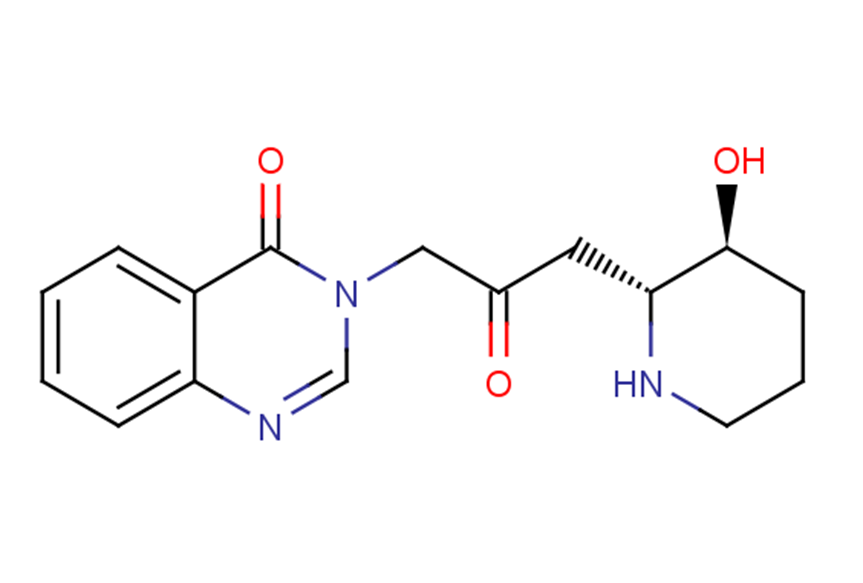
Febrifugine
CAS No. 24159-07-7
Febrifugine( —— )
Catalog No. M22424 CAS No. 24159-07-7
Febrifugine is an effective coccidiostat, possesses schizonticide props; it and its derivatives shows high degree of antimalarial activity but use limited by toxicity.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 427 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameFebrifugine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionFebrifugine is an effective coccidiostat, possesses schizonticide props; it and its derivatives shows high degree of antimalarial activity but use limited by toxicity.
-
DescriptionFebrifugine is an effective coccidiostat, possesses schizonticide props; it and its derivatives shows high degree of antimalarial activity but use limited by toxicity .
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayMicrobiology/Virology
-
TargetAntifection
-
RecptorAntifection|IL Receptor
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number24159-07-7
-
Formula Weight301.34
-
Molecular FormulaC16H19N3O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 25 mg/mL (82.96 mM)
-
SMILESO[C@H]1CCCN[C@@H]1CC(=O)Cn1cnc2ccccc2c1=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Pyrolin
Pyrolin has a strong antifungal activity and exerts a potent impact on the ultrastructure of M.fructicola.
-
Desciclovir
Desciclovir (DCV), a prodrug of the antiherpetic agent acyclovir (ACV), is converted in humans to ACV, presumably by xanthine oxidase.
-
Octahydrocurcumin
Octahydrocurcumin has antioxidant and and anti-inflammatory activities, it can inhibit the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory response via the mechanism of inhibiting NF-kB translocation to the nucleus.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


