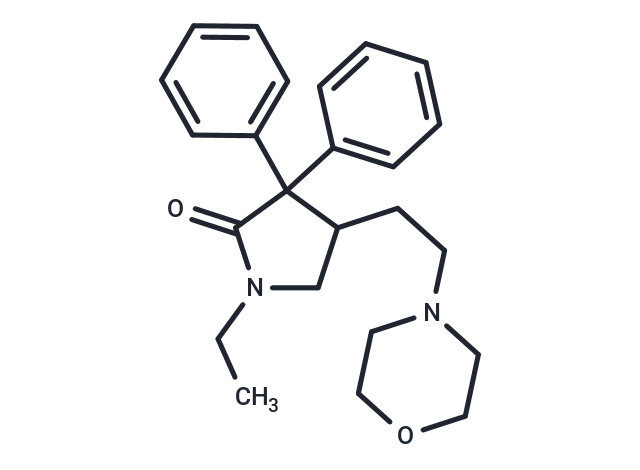
Doxapram
CAS No. 309-29-5
Doxapram( —— )
Catalog No. M33801 CAS No. 309-29-5
Doxapram (Dopram) is a respiratory stimulant that inhibits TASK-1, TASK-3, and TASK-1/TASK-3 heterodimer channels and is used to study ventilatory failure caused by apnea of ??prematurity and exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 55 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 72 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 104 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 165 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 242 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 349 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 520 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDoxapram
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDoxapram (Dopram) is a respiratory stimulant that inhibits TASK-1, TASK-3, and TASK-1/TASK-3 heterodimer channels and is used to study ventilatory failure caused by apnea of ??prematurity and exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
-
DescriptionDoxapram inhibits TASK-1, TASK-3, TASK-1/TASK-3 heterodimeric channel function with EC50 of 410 nM, 37 μM, 9 μM, respectively.Target: Potassium Channel Doxapram is a respiratory stimulant. Doxapram (15-150 microM) also evoked 3H overflow in a concentration dependent manner, and doxapram-evoked release was inhibited by the Ca2+ channel blocker nifedipine (5 microM). Analysis of released tritiated compounds suggested that doxapram preferentially stimulated the release of dopamine. Our results indicate that the mechanism of action of doxapram shares similarities with that of hypoxia in the carotid body . Doxapram (1-100 microM) caused rapid, reversible and dose-dependent inhibitions of K+ currents recorded in type I cells (IC50 approximately 13 microM). doxapram was also seen to directly inhibit Ca(2+)-independent K+ currents. Doxapram was a more potent inhibitor of the Ca(2+)-activated K+ currents recorded under control conditions. Doxapram (10 microM) was without effect on L-type Ca2+ channel currents recorded under conditions where K+ channel activity was minimized and was also without significant effect on K+ currents recorded in the neuronal cell line NG-108 15, suggesting a selective effect on carotid body type I cells. The effects of doxapram on type I cells show similarities to those of the physiological stimuli of the carotid body, suggesting that doxapram may share a similar mechanism of action in stimulating the intact organ .
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayCell Cycle/DNA Damage
-
TargetPotassium Channel
-
RecptorPotassium Channel
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number309-29-5
-
Formula Weight378.51
-
Molecular FormulaC24H30N2O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESO=C1N(CC)CC(CCN2CCOCC2)C1(C=3C=CC=CC3)C=4C=CC=CC4
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Cotten JF, et al. The ventilatory stimulant doxapram inhibits TASK tandem pore (K2P) potassium channel function but does not affect minimum alveolar anesthetic concentration. Anesth Analg, 2006, 102(3), 779-785.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
Gut restricted-7
Gut restricted-7 (GR-7) is a covalent and orally active pan-bile salt hydrolase (BSH) inhibitor. It decreases gut bacterial BSHs and decreases deconjugated bile acid levels in the feces of mice.
-
Doxapram hydrochlori...
Doxapram hydrochloride hydrate inhibits TASK-1, TASK-3, TASK-1/TASK-3 heterodimeric channel function with EC50 of 410 nM, 37 μM, 9 μM, respectively.
-
Kv3 modulator 1
Kv3 modulator 1 is a voltage-gated potassium channel Kv3 modulator that can be used to study neurologic-level diseases.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


