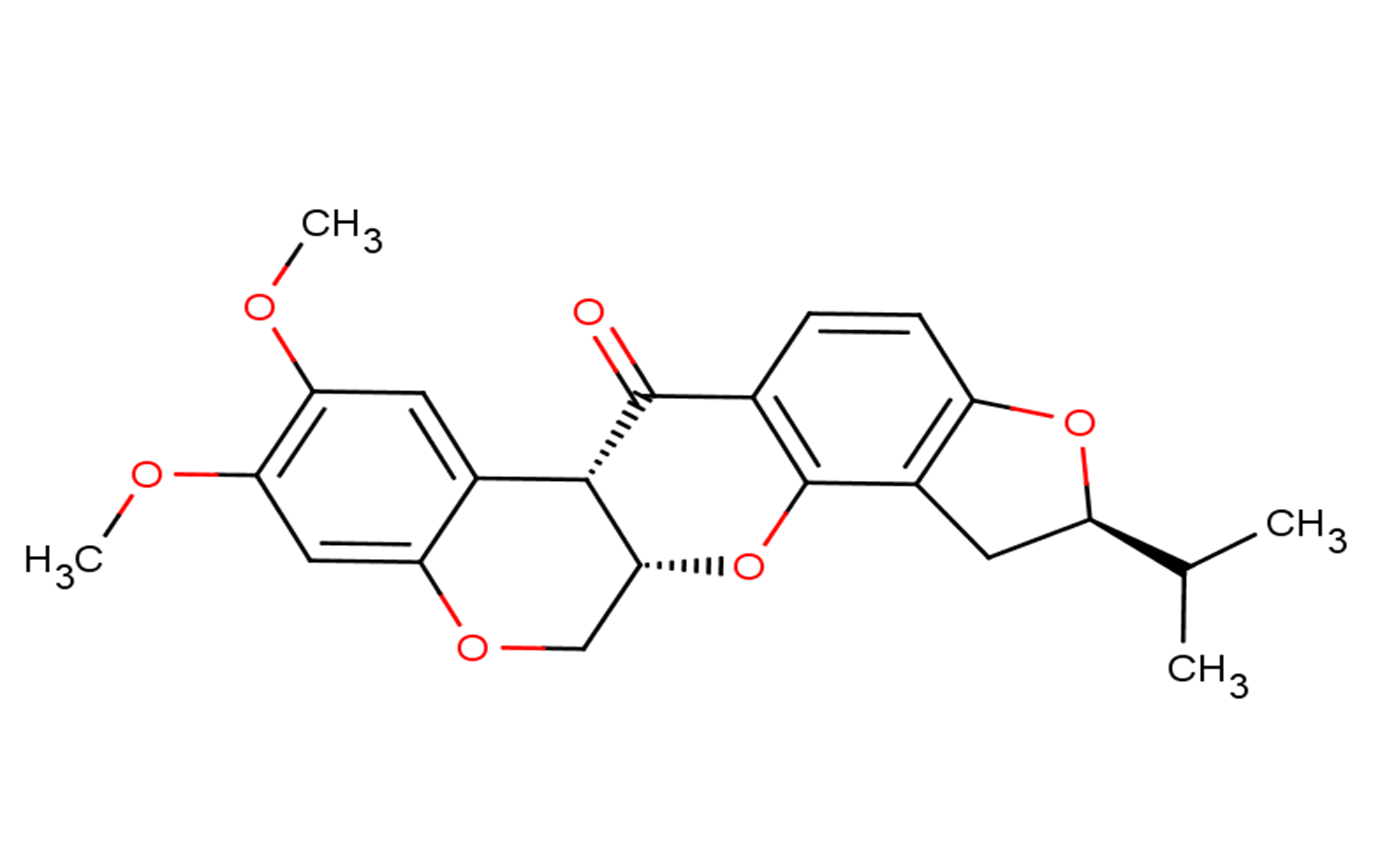
Dihydrorotenone
CAS No. 6659-45-6
Dihydrorotenone( —— )
Catalog No. M24675 CAS No. 6659-45-6
Dihydrorotenone is a potent mitochondrial inhibitor and probably induces Parkinsonian syndrome.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 251 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 399 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 660 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 888 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDihydrorotenone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDihydrorotenone is a potent mitochondrial inhibitor and probably induces Parkinsonian syndrome.
-
DescriptionDihydrorotenone is a potent mitochondrial inhibitor and probably induces Parkinsonian syndrome.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayApoptosis
-
TargetApoptosis
-
RecptorApoptosis|Mitochondrial Metabolism
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number6659-45-6
-
Formula Weight396.43
-
Molecular FormulaC23H24O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10 mM
-
SMILESCC(C)[C@H]1CC2=C(O1)C=CC3=C2O[C@@H]4COC5=CC(=C(C=C5[C@@H]4C3=O)OC)OC
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Natural pesticide dihydrorotenone arrests human plasma cancer cells at the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2014 May;28(5):232-8.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Elesclomol
Elesclomol (STA-4783) is a small-molecule oxidative stress inducer.
-
Oenothein B
Oenothein B is a specific inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase. Oenothein B shows antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antifungal, anti-HCV, and antitumor properties.
-
3-Deoxyaconitine
3-?Deoxyaconitine is a derivative of Aconitine (A189875), which activates tetrodotoxin-sensitive Na+ channels, inducing presynaptic depolarization.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


