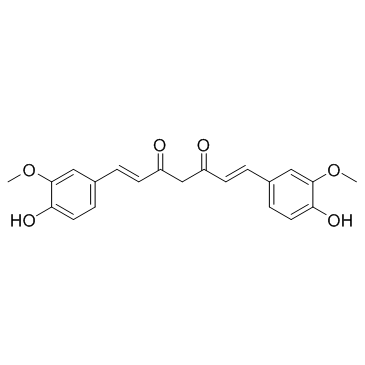
Curcumin
CAS No. 458-37-7
Curcumin( Indian Saffron | Turmeric yellow )
Catalog No. M14544 CAS No. 458-37-7
Curcumin is a natural phenolic compound with impressive antioxidant properties. Curcumin is recently proved to exert its chemopreventive effects partly through the activation of nuclear factor (erythroid-2 related) factor 2 (Nrf2).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | 27 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 34 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 51 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 79 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCurcumin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCurcumin is a natural phenolic compound with impressive antioxidant properties. Curcumin is recently proved to exert its chemopreventive effects partly through the activation of nuclear factor (erythroid-2 related) factor 2 (Nrf2).
-
DescriptionCurcumin is a natural phenolic compound with impressive antioxidant properties. Curcumin is recently proved to exert its chemopreventive effects partly through the activation of nuclear factor (erythroid-2 related) factor 2 (Nrf2).(In Vitro):Curcumin exerts its chemopreventive effects partly through the activation of nuclear factor (erythroid-2 related) factor 2 (Nrf2) and its antioxidant and phase II detoxifying enzymes. Curcumin inhibits T47D cells growth, with IC50s of 25, 19 and 17.5 μM for 24, 48 and 72 h MTT assays respectively. IC50s of curcumin and silibinin mixture against T47D cells, are 17.5, 15, and 12 μM for 24, 48, and 72 h exposure times, respectively. Curcumin (2.5-80 μM) induces apoptotic cell death in AGS and HT-29 cell lines, and the IC50 is 21.9±0.1, 40.7±0.5 μM, respectively, in both AGS and HT-29 cell lines. Curcumin-induced apoptosis requires caspase activities in AGS and HT-29 cells. Curcumin induces ER Ca2+ decline and mitochondrial Ca2+ overloading. Curcumin induces the G2/M cell cycle arrest of LNCaP and PC-3 cells in a dose dependent manner. Curcumin upregulates the protein level of NF-kappaB inhibitor IkappaBalpha and downregulates protein levels of c-Jun and AR. (In Vivo):Curcumin (10 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly prevents decrease in the percentage of sucrose consumption, as compared to the CMS-exposed rats. Curcumin treatment results in significant prevention of increase in TNF-α and IL-6 levels in stressed rats. Curcumin decreases binding of p300/CREB-binding protein (CBP) at the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) promoter at 20 mg/kg (i.p.), reduces binding of P300/CBP at the BDNF promoter at 40 mg/kg, and decreases binding all the four proteins of p300/CBP and H3K9ac/H4K5ac at the BDNF promoter at 60 mg/kg in chronic constriction injury (CCI) rats.
-
In VitroCurcumin exerts its chemopreventive effects partly through the activation of nuclear factor (erythroid-2 related) factor 2 (Nrf2) and its antioxidant and phase II detoxifying enzymes. Curcumin inhibits T47D cells growth, with IC50s of 25, 19 and 17.5 μM for 24, 48 and 72 h MTT assays respectively. IC50s of curcumin and silibinin mixture against T47D cells, are 17.5, 15, and 12 μM for 24, 48, and 72 h exposure times, respectively. Curcumin (2.5-80 μM) induces apoptotic cell death in AGS and HT-29 cell lines, and the IC50 is 21.9±0.1, 40.7±0.5 μM, respectively, in both AGS and HT-29 cell lines. Curcumin-induced apoptosis requires caspase activities in AGS and HT-29 cells. Curcumin induces ER Ca2+ decline and mitochondrial Ca2+ overloading. Curcumin induces the G2/M cell cycle arrest of LNCaP and PC-3 cells in a dose dependent manner. Curcumin upregulates the protein level of NF-kappaB inhibitor IkappaBalpha and downregulates protein levels of c-Jun and AR.
-
In VivoCurcumin (10 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly prevents decrease in the percentage of sucrose consumption, as compared to the CMS-exposed rats. Curcumin treatment results in significant prevention of increase in TNF-α and IL-6 levels in stressed rats. Curcumin decreases binding of p300/CREB-binding protein (CBP) at the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) promoter at 20 mg/kg (i.p.), reduces binding of P300/CBP at the BDNF promoter at 40 mg/kg, and decreases binding all the four proteins of p300/CBP and H3K9ac/H4K5ac at the BDNF promoter at 60 mg/kg in chronic constriction injury (CCI) rats.
-
SynonymsIndian Saffron | Turmeric yellow
-
PathwayChromatin/Epigenetic
-
TargetEpigenetic Reader Domain
-
Recptorp300 histone acetylatransferase| KEAP1-Nrf2
-
Research AreaOther Indications
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number458-37-7
-
Formula Weight368.39
-
Molecular FormulaC21H20O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 73mg/ml (198.16 mM); Water: <1mg/ml; Ethanol: <1mg/ml
-
SMILESO=C(CC(/C=C/C1=CC=C(O)C(OC)=C1)=O)/C=C/C2=CC=C(O)C(OC)=C2
-
Chemical Name(1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Zanotto-Filho A, et al. Y Lett. 2015 Mar 28;358(2):220-3
molnova catalog



related products
-
SGC2085 HCl
SGC2085 is a potent and selective coactivator associated arginine methyltransferase 1 (CARM1) Inhibitor with an IC50 of 50 nM and more than undred-fold selectivity over other PRMTs.
-
Butyrolactone 3
Butyrolactone 3 (MB-3) is a histone acetyltransferase Gcn5 inhibitor with a weak affinity for CBP.Butyrolactone 3 has antimicrobial activity and has been used in cancer, metabolic and neurological disorders.
-
GSK046
GSK046 is a potent, selective and orally active BD2 bromodomain inhibitor of the BET proteins(IC50s of 264 nM (BRD2 BD2), 98 nM (BRD3 BD2), 49 nM (BRD4 BD2) and 214 nM (BRDT BD2), respectively).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


