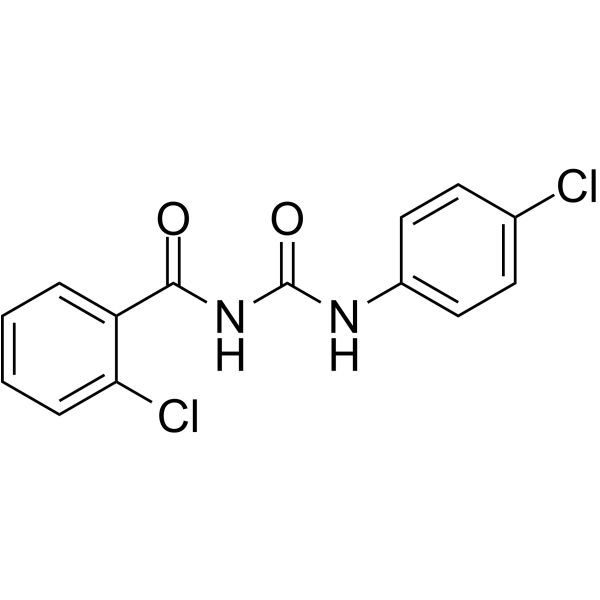
Chlorobenzuron
CAS No. 57160-47-1
Chlorobenzuron( —— )
Catalog No. M28322 CAS No. 57160-47-1
Chlorobenzuron is a chitin synthetase inhibitor, acts as an insecticide. Chlorobenzuron can inhibit larvae development and pupate.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 45 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameChlorobenzuron
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionChlorobenzuron is a chitin synthetase inhibitor, acts as an insecticide. Chlorobenzuron can inhibit larvae development and pupate.
-
DescriptionChlorobenzuron is a chitin synthetase inhibitor, acts as an insecticide. Chlorobenzuron can inhibit larvae development and pupate.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number57160-47-1
-
Formula Weight309.15
-
Molecular FormulaC14H10Cl2N2O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESClc1ccc(NC(=O)NC(=O)c2ccccc2Cl)cc1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Wu P, et al. Supercritical fluid extraction assisted isolation of sesquiterpene lactones with antiproliferative effects from Centipeda minima. Phytochemistry. 2012 Apr;76:133-40.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Stachyose
Stachyose is a natual productit highly promotes proliferation of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) by inducing LAB to produce more α-galactosidase to hydrolyze stachyose.
-
Oseltamivir acid met...
Oseltamivir acid methyl ester hydrochloride is a precursor form of oseltamivir acid. Oseltamivir acid methyl ester is converted to oseltamivir acid converted by carboxylesterase 1 (CES1).
-
WR-99210
WR-99210 is a potent inhibitor of?Plasmodium falciparum?dihydrofolate reductase (pfDHFR), which is a major malarial drug target.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


