CS3
CAS No. 1207457-11-1
CS3( cIAP inhibitor CS3 )
Catalog No. M10766 CAS No. 1207457-11-1
CS3 is a potent, selective cIAP1 and cIAP2 inhibitor with IC50 of 16 nM and 85 nM respectively.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCS3
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCS3 is a potent, selective cIAP1 and cIAP2 inhibitor with IC50 of 16 nM and 85 nM respectively.
-
DescriptionCS3 is a potent, selective cIAP1 and cIAP2 inhibitor with IC50 of 16 nM and 85 nM respectively, shows no significant activity against XIAP (IC50>34 uM).
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymscIAP inhibitor CS3
-
PathwayApoptosis
-
TargetIAP
-
RecptorIAP
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1207457-11-1
-
Formula Weight506.651
-
Molecular FormulaC28H38N6O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
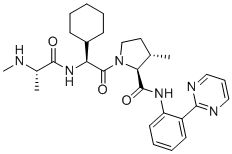
Chemical Name(2S,3S)-1-((S)-2-cyclohexyl-2-((S)-2-(methylamino)propanamido)acetyl)-3-methyl-N-(2-(pyrimidin-2-yl)phenyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Ndubaku C, et al. ACS Chem Biol. 2009 Jul 17;4(7):557-66.
molnova catalog



related products
-
GDC-0152
GDC-0152 is a potent antagonist of XIAP-BIR3, ML-IAP-BIR3, cIAP1-BIR3 and cIAP2-BIR3 with Ki of 28 nM, 14 nM, 17 nM and 43 nM, respectively.
-
BV6
A small molecule, bivalent IAP antagonist that binds to the c-IAP1 and XIAP BIR2-BIR3 domains.
-
SM-164
SM-164 binds to XIAP protein containing both the BIR2 and BIR3 domains (IC50: 1.39 nM). It acts as an extremely potent antagonist of XIAP. SM-164 binds to XIAP being 300 and 7000-times more potent than its monovalent counterparts and the natural Smac AVPI peptide, respectively.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


