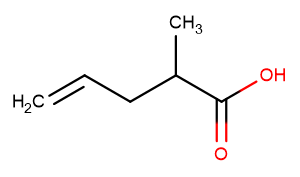
2-Methyl-4-pentenoic Acid
CAS No. 1575-74-2
2-Methyl-4-pentenoic Acid( 2-Methylpent-4-enoic acid )
Catalog No. M21378 CAS No. 1575-74-2
2-Methyl-4-pentenoic acid is a branched-chain fatty acid.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 29 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 36 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name2-Methyl-4-pentenoic Acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description2-Methyl-4-pentenoic acid is a branched-chain fatty acid.
-
Description2-Methyl-4-pentenoic acid is a branched-chain fatty acid.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms2-Methylpent-4-enoic acid
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1575-74-2
-
Formula Weight114.14
-
Molecular FormulaC6H10O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (876.12 mM)
-
SMILESCC(CC=C)C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
6-Hydroxyluteolin
6-Hydroxyluteolin (Compound 17) is a flavonoid compound. 6-Hydroxyluteolin has an inhibitory effect on aldose reductase (AR) .
-
3-Feruloyl-1-Sinapoy...
3-Feruloyl-1-Sinapoyl sucrose (compound 1) is a glycoside isolated from the aerial parts of Polygala chamaebuxus.
-
Ac-Endothelin-1 (16-...
Ac-Endothelin-1 (16-21), human



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


