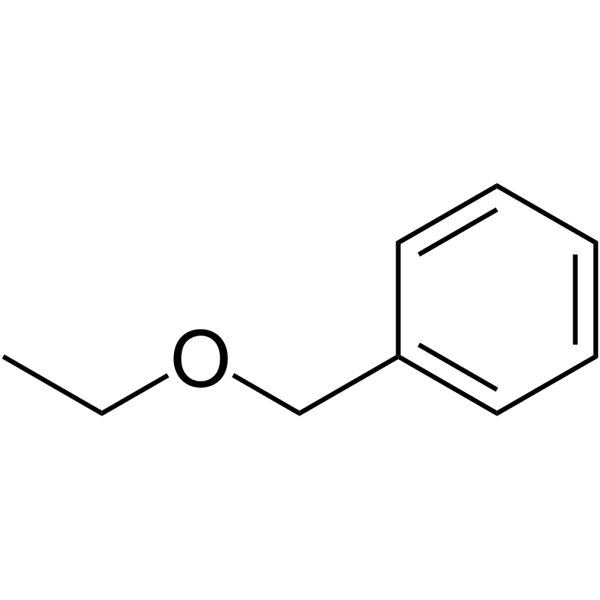
(Ethoxymethyl)benzene
CAS No. 539-30-0
(Ethoxymethyl)benzene( —— )
Catalog No. M28093 CAS No. 539-30-0
(Ethoxymethyl)benzene is a human endogenous metabolite.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 27 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name(Ethoxymethyl)benzene
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description(Ethoxymethyl)benzene is a human endogenous metabolite.
-
Description(Ethoxymethyl)benzene is a human endogenous metabolite.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number539-30-0
-
Formula Weight136.194
-
Molecular FormulaC9H12O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (734.27 mM)
-
SMILESCCOCc1ccccc1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Saka M, et al. Application of an amphibian (Silurana tropicalis) metamorphosis assay to the testing of the chronic toxicity of three rice paddy herbicides: simetryn, mefenacet, and thiobencarb. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2013 Jun;92:135-43.
molnova catalog



related products
-
D-Mannose
D-Mannose is a carbohydrate which plays an important role in human metabolism especially in the glycosylation of specific proteins.
-
3-Hydroxybutyric aci...
3-Hydroxybutyric acid (or beta-hydroxybutyrate) is a ketone body. Like the other ketone bodies (acetoacetate and acetone) levels of 3-hydroxybutyrate in blood and urine are raised in ketosis. In humans 3-hydroxybutyrate is synthesized in the liver from acetyl-CoA and can be used as an energy source by the brain when blood glucose is low.
-
L-Citrulline
L-Citrulline is an amino acid derived from ornithine in the catabolism of proline or glutamine and glutamate or from l-arginine via arginine-citrulline pathway.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


