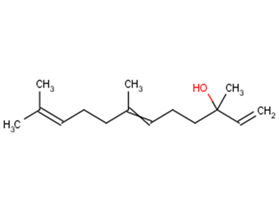
nerolidol
CAS No. 7212-44-4
nerolidol( BRN 1724135 | BRN1724135 | BRN 1724135 )
Catalog No. M19035 CAS No. 7212-44-4
Nerolidol shows sedative effects in animals, oxidative process plays a crucial role on neuronal pathological consequence.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Namenerolidol
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionNerolidol shows sedative effects in animals, oxidative process plays a crucial role on neuronal pathological consequence.
-
DescriptionNerolidol is a synthetic AChE inhibitor and F0F1-ATP synthase modulator. It acts as a sedative, inhibits growth of bacteria and fungi, and decreases the mitochondrial transmembrane electric potential to induce cell death in hepatocarcinoma cells.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsBRN 1724135 | BRN1724135 | BRN 1724135
-
PathwayMicrobiology/Virology
-
TargetHSV
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaOthers-Field
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number7212-44-4
-
Formula Weight222.37
-
Molecular FormulaC15H26O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (449.70 mM)
-
SMILESCC(=CCCC(=CCCC(C)(C=C)O)C)C
-
Chemical Name(R,E)-3,7,11-trimethyldodeca-1,6,10-trien-3-ol
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
nerolidol
Nerolidol shows sedative effects in animals, oxidative process plays a crucial role on neuronal pathological consequence.
-
Ardisiacrispin A
Ardisiacrispin A has cytotoxic activity toward HepG2 cancer cell with the GI(50) value of 1.56μM.
-
Acyclovir
An antiviral agent that competitively inhibits and inactivates HSV-specified DNA polymerases preventing further viral DNA synthesis without affecting the normal cellular processes.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


