MM-433593
CAS No. 1006604-91-6
MM-433593( —— )
Catalog No. M34337 CAS No. 1006604-91-6
MM-433593 is a selective fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH-1) inhibitor for the treatment of pain, inflammation, and other disorders.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 445 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 686 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 938 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 1398 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 1822 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 2250 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameMM-433593
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionMM-433593 is a selective fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH-1) inhibitor for the treatment of pain, inflammation, and other disorders.
-
DescriptionMM-433593 is a selective fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH-1) inhibitor for the treatment of pain, inflammation, and other disorders.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayMetabolic Enzyme/Protease
-
TargetFAAH
-
RecptorFAAH
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1006604-91-6
-
Formula Weight447.91
-
Molecular FormulaC25H22ClN3O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
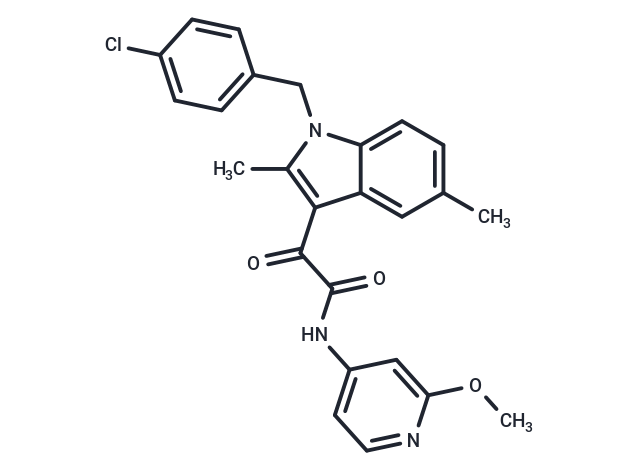
SMILESO=C(NC=1C=CN=C(OC)C1)C(=O)C=2C=3C=C(C=CC3N(C2C)CC4=CC=C(Cl)C=C4)C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
FAAH inhibitor 1
FAAH inhibitor 1 is an effective FAAH inhibitor with an IC50 of 18 nM.
-
Dual FAAH/sEH-IN-1
Dual FAAH/sEH-IN-1 is a dual inhibitor of sEH (soluble epoxide hydrolase) (IC50: 9.6 nM) and FAAH (fatty acid amide hydrolase) (IC50: 7 nM) with high affinity and anti-inflammatory activity.
-
URB-597
A potent and selective FAAH inhibitor with IC50 of 4.6 nM; increases anandamide levels in the brain of rats and wild-type mice (0.3 mg/kg i.p.); improves cognitive impairment by inhibiting mTOR-dependent autophagy in a CCH model.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


