Aminophylline
CAS No. 317-34-0
Aminophylline( Aminophylline, Aminophyllin | Theophyllamine | Cardophyllin | Phyllocontin )
Catalog No. M14036 CAS No. 317-34-0
Aminophylline is a competitive nonselective phosphodiesterase inhibitor that is used to treat airway obstruction from asthma or COPD.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 34 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 49 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 85 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAminophylline
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAminophylline is a competitive nonselective phosphodiesterase inhibitor that is used to treat airway obstruction from asthma or COPD.
-
DescriptionAminophylline is a competitive nonselective phosphodiesterase inhibitor that is used to treat airway obstruction from asthma or COPD.(In Vitro):Aminophylline is a compound of the bronchodilator theophylline with ethylenediamine in 2:1 ratio. The ethylenediamine improves solubility, and the aminophylline is usually found as a dihydrate. Aminophylline is less potent and shorter-acting than theophylline. Its most common use is in the treatment of airway obstruction from asthma or COPD. It is used off-label as a reversal agent during nuclear stress testing. Aminophylline is a nonselective adenosine receptor antagonist and phosphodiesterase inhibitor. Adenosine is an endogenous extracellular messenger that can regulate myocardial oxygen needs. It acts through cellular surface receptors which effect intracellular signalling pathways to increase coronary artery blood flow, slow heart rate, block atrioventricular node conduction, suppress cardiac automaticity, and decrease β-adrenergic effects on contractility. Adenosine also antagonizes chronotropic and ionotropic effects of circulating catecholamines. Overall, adenosine decreases the heart's rate and force of contraction, which increases blood supply to the cardiac muscle. Given specific circumstances this mechanism (which is intended to protect the heart) may cause atropine-resistant refractory bradyasystole. Adenosine's effects are concentration-dependent. Adenosine's receptors are competitively antagonized by methylxanthines such as aminophylline. Aminophylline competitively antagonizes the cardiac actions of adenosine at the cell surface receptors. Thus, it increases heart rate and contractility.
-
In VitroAminophylline is a compound of the bronchodilator theophylline with ethylenediamine in 2:1 ratio. The ethylenediamine improves solubility, and the aminophylline is usually found as a dihydrate. Aminophylline is less potent and shorter-acting than theophylline. Its most common use is in the treatment of airway obstruction from asthma or COPD. It is used off-label as a reversal agent during nuclear stress testing. Aminophylline is a nonselective adenosine receptor antagonist and phosphodiesterase inhibitor.Adenosine is an endogenous extracellular messenger that can regulate myocardial oxygen needs. It acts through cellular surface receptors which effect intracellular signalling pathways to increase coronary artery blood flow, slow heart rate, block atrioventricular node conduction, suppress cardiac automaticity, and decrease β-adrenergic effects on contractility. Adenosine also antagonizes chronotropic and ionotropic effects of circulating catecholamines. Overall, adenosine decreases the heart's rate and force of contraction, which increases blood supply to the cardiac muscle. Given specific circumstances this mechanism (which is intended to protect the heart) may cause atropine-resistant refractory bradyasystole. Adenosine's effects are concentration-dependent. Adenosine's receptors are competitively antagonized by methylxanthines such as aminophylline. Aminophylline competitively antagonizes the cardiac actions of adenosine at the cell surface receptors. Thus, it increases heart rate and contractility.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsAminophylline, Aminophyllin | Theophyllamine | Cardophyllin | Phyllocontin
-
PathwayAngiogenesis
-
TargetPDE
-
RecptorPDE
-
Research AreaInflammation/Immunology
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number317-34-0
-
Formula Weight420.43
-
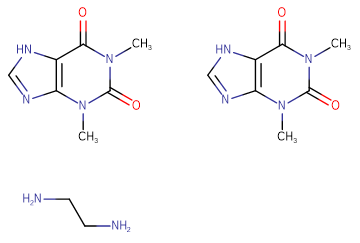
Molecular Formula2C7H8O2·C2H8N2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityWater: 84 mg/mL (199.79 mM); DMSO: 53 mg/mL (126.06 mM)
-
SMILESCN1C2=C(NC=N2)C(N(C)C1=O)=O.CN3C4=C(NC=N4)C(N(C)C3=O)=O.NCCN
-
Chemical Name1,3-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione compound with ethane-1,2-diamine (2:1)
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Hirota K, et al. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2002 Mar;46(3):297-302.
molnova catalog



related products
-
PF-8380
Potent autotaxin inhibitor (IC50?= 2.8 nM in isolated enzyme assay; 101 nM in human whole blood).
-
Gisadenafil
Gisadenafil is a selective inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) with an IC50 of 3.6 nM and prevents degradation of cGMP.
-
Torbafylline
Torbafylline, a xanthine derivative, is a phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor that attenuates burn-induced protein hydrolysis in rat skeletal muscle through activation of the PDE4/cAMP/EPAC/PI3K/Akt pathway.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


